This is a preprint.
Brain Vasculature Accumulates Tau and Is Spatially Related to Tau Tangle Pathology in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 38328111
- PMCID: PMC10849642
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.27.577088
Brain Vasculature Accumulates Tau and Is Spatially Related to Tau Tangle Pathology in Alzheimer's Disease
Update in
-
Brain vasculature accumulates tau and is spatially related to tau tangle pathology in Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Jun 17;147(1):101. doi: 10.1007/s00401-024-02751-9. Acta Neuropathol. 2024. PMID: 38884806 Free PMC article.
Abstract
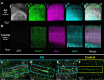
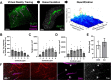
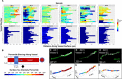
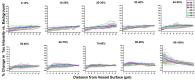
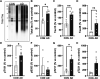
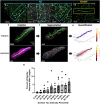
Insoluble pathogenic proteins accumulate along blood vessels in conditions of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), exerting a toxic effect on vascular cells and impacting cerebral homeostasis. In this work we provide new evidence from three-dimensional human brain histology that tau protein, the main component of neurofibrillary tangles, can similarly accumulate along brain vascular segments. We quantitatively assessed n=6 Alzheimer's disease (AD), and n=6 normal aging control brains and saw that tau-positive blood vessel segments were present in all AD cases. Tau-positive vessels are enriched for tau at levels higher than the surrounding tissue and appear to affect arterioles across cortical layers (I-V). Further, vessels isolated from these AD tissues were enriched for N-terminal tau and tau phosphorylated at T181 and T217. Importantly, tau-positive vessels are associated with local areas of increased tau neurofibrillary tangles. This suggests that accumulation of tau around blood vessels may reflect a local clearance failure. In sum, these data indicate tau, like amyloid beta, accumulates along blood vessels and may exert a significant influence on vasculature in the setting of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; blood vessels; cerebral amyloid angiopathy; cerebral vasculature; neurofibrillary tangles; tau.
Conflict of interest statement
BTH has a family member who works at Novartis and owns stock in Novartis; he serves on the SAB of Dewpoint and owns stock. He serves on a scientific advisory board or is a consultant for AbbVie, Avrobio, Axon, Biogen, BMS Cell Signaling, Genentech, Ionis, Novartis, Seer, Takeda, the US Dept of Justice, Vigil, Voyager. His laboratory is supported by Sponsored research agreements with AbbVie, F Prime, and research grants from the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund, Tau Consortium, and the JPB Foundation. REB works on the AbbVie-Hyman Collaboration. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lewis DA, Campbell MJ, Terry RD, Morrison JH. Laminar and regional distributions of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in Alzheimer’s disease: a quantitative study of visual and auditory cortices. J Neurosci. 1987;7(6):1799–808. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01799.1987. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tarasoff-Conway JM, Carare RO, Osorio RS, Glodzik L, Butler T, Fieremans E, Axel L, Rusinek H, Nicholson C, Zlokovic BV, Frangione B, Blennow K, Menard J, Zetterberg H, Wisniewski T, de Leon MJ. Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11(8):457–70. Epub 20150721. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
