This is a preprint.
Diagnostically distinct resting state fMRI energy distributions: A subject-specific maximum entropy modeling study
- PMID: 38328170
- PMCID: PMC10849576
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.23.576937
Diagnostically distinct resting state fMRI energy distributions: A subject-specific maximum entropy modeling study
Abstract
Objective: Existing neuroimaging studies of psychotic and mood disorders have reported brain activation differences (first-order properties) and altered pairwise correlation-based functional connectivity (second-order properties). However, both approaches have certain limitations that can be overcome by integrating them in a pairwise maximum entropy model (MEM) that better represents a comprehensive picture of fMRI signal patterns and provides a system-wide summary measure called energy. This study examines the applicability of individual-level MEM for psychiatry and identifies image-derived model coefficients related to model parameters.
Method: MEMs are fit to resting state fMRI data from each individual with schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, and major depression (n=132) and demographically matched healthy controls (n=132) from the UK Biobank to different subsets of the default mode network (DMN) regions.
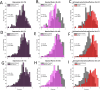
Results: The model satisfactorily explained observed brain energy state occurrence probabilities across all participants, and model parameters were significantly correlated with image-derived coefficients for all groups. Within clinical groups, averaged energy level distributions were higher in schizophrenia/schizoaffective disorder but lower in bipolar disorder compared to controls for both bilateral and unilateral DMN. Major depression energy distributions were higher compared to controls only in the right hemisphere DMN.
Conclusions: Diagnostically distinct energy states suggest that probability distributions of temporal changes in synchronously active nodes may underlie each diagnostic entity. Subject-specific MEMs allow for factoring in the individual variations compared to traditional group-level inferences, offering an improved measure of biologically meaningful correlates of brain activity that may have potential clinical utility.
Keywords: Bipolar disorder; Computational psychiatry; Generalized Ising model; Major depression; Network neuroscience; Schizophrenia; Transdiagnostic approach.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors declare no conflicts of interest associated with this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Precision medicine for mood disorders: objective assessment, risk prediction, pharmacogenomics, and repurposed drugs.Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Jul;26(7):2776-2804. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01061-w. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Mol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33828235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amit DJ, Gutfreund H, Sompolinsky H (1985): Spin-glass models of neural networks. Phys Rev A Gen Phys. 32:1007–1018. - PubMed
-
- Chialvo DR (2010): Emergent complex neural dynamics. Nature Physics. 6:744–750.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
