This is a preprint.
Epidermal ZBP1 stabilizes mitochondrial Z-DNA to drive UV-induced IFN signaling in autoimmune photosensitivity
- PMID: 38328232
- PMCID: PMC10849619
- DOI: 10.1101/2024.01.23.576771
Epidermal ZBP1 stabilizes mitochondrial Z-DNA to drive UV-induced IFN signaling in autoimmune photosensitivity
Update in
-
Epidermal ZBP1 stabilizes mitochondrial Z-DNA to drive UV-induced IFN signaling in autoimmune photosensitivity.Sci Immunol. 2025 Mar 7;10(105):eado1710. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.ado1710. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Sci Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40053607
Abstract
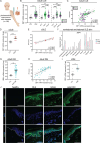
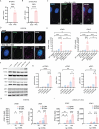
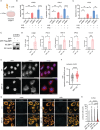
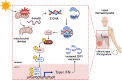
Photosensitivity is observed in numerous autoimmune diseases and drives poor quality of life and disease flares. Elevated epidermal type I interferon (IFN) production primes for photosensitivity and enhanced inflammation, but the substrates that sustain and amplify this cycle remain undefined. Here, we show that IFN-induced Z-DNA binding protein 1 (ZBP1) stabilizes ultraviolet (UV)B-induced cytosolic Z-DNA derived from oxidized mitochondrial DNA. ZBP1 is significantly upregulated in the epidermis of adult and pediatric patients with autoimmune photosensitivity. Strikingly, lupus keratinocytes accumulate extensive cytosolic Z-DNA after UVB, and transfection of keratinocytes with Z-DNA results in stronger IFN production through cGAS-STING activation compared to B-DNA. ZBP1 knockdown abrogates UV-induced IFN responses, whereas overexpression results in a lupus-like phenotype with spontaneous Z-DNA accumulation and IFN production. Our results highlight Z-DNA and ZBP1 as critical mediators for UVB-induced inflammation and uncover how type I IFNs prime for cutaneous inflammation in photosensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JMK has received grant support from Q32 Bio, Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, Ventus Therapeutics, Rome Therapeutics, and Janssen. JMK has served on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, EMD serrano, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Aurinia Pharmaceuticals, Rome Therapeutics, and Ventus Therapeutics. JEG has received support from Eli Lilly, Janssen, BMS, Sanofi, Prometheus, Almirall, Kyowa-Kirin, Novartis, AnaptysBio, Boehringer Ingelheim, Regeneron, AbbVie, and Galderma.
Figures



References
-
- Wenzel J., Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: new insights into pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 15, 519–532 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
