Biodegradable Nanocomposite of ZnS(Mn) Quantum Dots Immobilized Graphene Oxide for Bioimaging Applications
- PMID: 38328615
- PMCID: PMC10845254
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.87536
Biodegradable Nanocomposite of ZnS(Mn) Quantum Dots Immobilized Graphene Oxide for Bioimaging Applications
Abstract
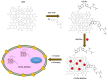
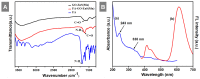
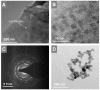
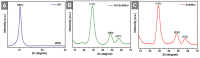
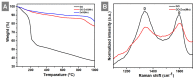
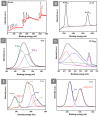
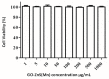
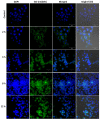
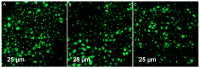
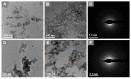
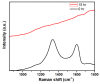
Developing a biocompatible and biodegradable graphene-based fluorescent nanoprobe with the ability to visualize live cells could be interesting for intracellular imaging and monitoring the efficiency of chemotherapy. Herein, we report a biodegradable and biocompatible hybrid fluorescent graphene oxide (GO)-ZnS(Mn) composite synthesized via in situ growth of ZnS(Mn) quantum dots (QDs) on the surface of GO in the aqueous medium. The prepared 'GO-ZnS(Mn)' composite was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM) along with selected area electron diffraction (SAED). Further, the fluorescence properties of the GO-ZnS(Mn) composite were studied using fluorescence emission spectroscopy. The composite material exhibited a strong and broad visible light fluorescence from 500 to 600 nm by excitation with 365 nm (UV) light. The cytotoxic experiments of folic acid (FA) conjugated GO-ZnS(Mn) using MTT [(3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide)] assay revealed that the composite had excellent biocompatibility even at higher concentrations up to 200 µg/mL in HeLa cell lines. Next, the bioimaging experiments carried out using confocal fluorescence laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) revealed that GO-ZnS(Mn) composite was taken up by the HeLa cells effectively within 12 h of incubation via receptor (folate) mediated endocytosis with strong fluorescence throughout the cell surface. Finally, the biodegradability of GO-ZnS(Mn) composite was studied by treating it with human myeloperoxidase enzyme (hMPO) isolated from the primary immune cells, neutrophils, which is important to understand the in vivo fate of GO-Zns(Mn). The HR-TEM and Raman analyses confirmed the biodegradation of GO-ZnS(Mn) within 15 h of hMPO treatment. Thus, the biodegradable GO-ZnS (Mn) composite could be helpful for chemotherapy and bioimaging applications.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Li J, Pant A, Chin CF, Ang WH, Ménard-Moyon C, Nayak TR. et al. In vivo biodistribution of platinum-based drugs encapsulated into multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Nanomedicine: NBM. 2014;10:1465–75. - PubMed
-
- Kurapati R, Martìn C, Palermo V, Nishina Y, Bianco A. Biodegradation of graphene materials catalyzed by human eosinophil peroxidase. Faraday Discuss. 2021;227:189–203. - PubMed
-
- Ma B, Martín C, Kurapati R, Bianco A. Degradation-by-design: how chemical functionalization enhances the biodegradability and safety of 2D materials. Chem Soc Rev. 2020;49:6224–47. - PubMed
-
- Chung C, Kim Y-K, Shin D, Ryoo S-R, Hong BH, Min D-H. Biomedical Applications of Graphene and Graphene Oxide. Acc Chem Res. 2013;46:2211–24. - PubMed
-
- Pan Y, Sahoo NG, Li L. The application of graphene oxide in drug delivery. Expert Opin Drug Del. 2012;9:1365–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

