Validation of targeted next-generation sequencing panels in a cohort of Polish patients with epilepsy: assessing variable performance across clinical endophenotypes and uncovering novel genetic variants
- PMID: 38328757
- PMCID: PMC10849089
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1316933
Validation of targeted next-generation sequencing panels in a cohort of Polish patients with epilepsy: assessing variable performance across clinical endophenotypes and uncovering novel genetic variants
Abstract
Introduction: Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Panels (TNGSP) have become a standard in global clinical practice. Instead of questioning the necessity of next-generation sequencing in epilepsy patients, contemporary large-scale research focuses on factors such as the size of TNGSP, the comparative advantages of exome or genome-wide sequencing over TNGSP, and the impact of clinical, electrophysiological, and demographic variables on genetic test performance. This study aims to elucidate the demographic and clinical factors influencing the performance of TNGSP in 138 Polish patients with epilepsy, recognizing the pivotal role of genetic testing in guiding patient management and therapy.
Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on patients from a genetic clinic in Poznań, Poland, who underwent commercial gene panel studies at Invitae Corporation (USA) between 2020 and 2022. Patient groups were defined based on the age of onset of the first epileptic seizures, seizure type, gender, fever dependence of seizures, presence of intellectual disability or developmental delay, abnormalities in MRI, and the presence of dysmorphic features or congenital malformations. Seizure classification followed the 2017 ILAE criteria.
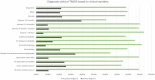
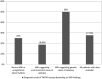
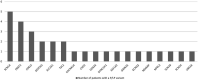
Results: Among the 138 patients, 30 (21.7%) exhibited a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant, with a distribution of 20.7% in males and 22.5% in females. Diagnostic performance correlated with the patient's age at the onset of the first seizure and the type of seizure. Predominant variants were identified in the SCN1A, PRRT2, CDKL5, DEPDC5, TSC2, and SLC2A1 genes. Additionally, 12 genes (CACNA1A, SCN2A, GRIN2A, KCNQ2, CHD2, DYNC1H1, NEXMIF, SCN1B, DDX3X, EEF1A2, NPRL3, UBE3A) exhibited single instances of damage. Notably, novel variants were discovered in DEPDC5, SCN1A, TSC2, CDKL5, NPRL3, DYNC1H1, CHD2, and DDX3X.
Discussion: Identified variants were present in genes previously recognized in both European and non-European populations. A thorough examination of Variants of Uncertain Significance (VUSs), specifically focusing on gene copy number changes, may unveil more extensive chromosomal aberrations. The relatively frequent occurrence of pathological variants in X chromosome-linked genes in girls warrants further investigation, challenging the prevailing notion of male predominance in X-linked epilepsy.
Keywords: ILAE; epilepsy; genetics; next-generation sequencing; panels; yield.
Copyright © 2024 Badura-Stronka, Wołyńska, Winczewska-Wiktor, Marcinkowska, Karolewska, Tomkowiak-Kędzia, Piechota, Przyborska, Kochalska and Steinborn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Application of Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Panels and Whole Exome Sequencing in Childhood Epilepsy.Neuroscience. 2019 Oct 15;418:291-310. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.08.016. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 31487502
-
Impact of Genetic Testing Using Gene Panels, Exomes, and Genome Sequencing in Romanian Children with Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 19;26(10):4843. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104843. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429983 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Yield From 339 Epilepsy Patients Screened on a Clinical Gene Panel.Pediatr Neurol. 2017 Dec;77:61-66. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Pediatr Neurol. 2017. PMID: 29056246 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical spectrum of KIAA2022/NEXMIF pathogenic variants in males and females: Report of three patients from Indian kindred with a review of published patients.Brain Dev. 2020 Oct;42(9):646-654. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2020.06.005. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Brain Dev. 2020. PMID: 32600841 Review.
-
Seizure features and outcomes in 50 children with GATOR1 variants: A retrospective study, more favorable for epilepsy surgery.Epilepsia Open. 2023 Sep;8(3):969-979. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12770. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Epilepsia Open. 2023. PMID: 37259768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NEXMIF overexpression is associated with autism-like behaviors and alterations in dendritic arborization and spine formation in mice.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jun 18;19:1556570. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1556570. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40606839 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Overview of the Current Status and Advancements in Various Treatment Strategies against Epilepsy.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Nov 1;7(12):3729-3757. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00494. eCollection 2024 Dec 13. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39698272 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

