Epidemiological study of hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad province (Iran) from 2008 to 2021: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38328787
- PMCID: PMC10848580
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.1812
Epidemiological study of hepatitis B and hepatitis C infection in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad province (Iran) from 2008 to 2021: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background and aims: Viral hepatitis is one of the top five reasons people die from infections all around the world. The present study aimed to assess the epidemiological features of hepatitis B and hepatitis C infections in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad province.
Methods: The data were obtained via the census method from the registered hepatitis B and hepatitis C data in the reportable disease care system of Yasuj University of Medical Sciences. The collected data are the result of serological tests. The χ 2 test was used to evaluate the important risk factors for hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. The joinpoint regression was performed to investigate the trend of HBV and HCV in recent years.
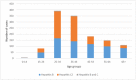
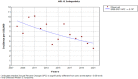
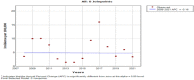
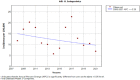
Results: Here, 1270 cases of hepatitis B and C were identified and reported in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad province from 2008 to 2021. The median age of patients was 38 (interquartile range: 31-51), varying significantly according to the type of hepatitis. The most common hepatitis in males was hepatitis C and in females, hepatitis B. Regarding the place of residence, HBV and HCV were both more prevalent in urban areas. The age group of 25-34 years has the highest prevalence of HBV and HCV. According to the joinpoint regression analysis, there is a decrease in the 14-year trend of incidence rate due to total hepatitis B and C: the annual percent change was -5.2% (95% confidence interval [CI]: -8.4 to -1.9, p = 0.005) for hepatitis B and -0.2% (95% CI: -10.7 to 11.6, p = 0.976) for hepatitis C.
Conclusion: This study shows the incidence rate of hepatitis B has been decreasing during the years of study but this trend has been stable for hepatitis C. Also, the highest number of cases of hepatitis B and C were reported in the age groups of 25-34 years. Hence, preventive interventions are vital in reducing the burden of these diseases.
Keywords: Kohgiluyeh and Boyer‐Ahmad; epidemiology; hepatitis B; hepatitis C; incidence.
© 2024 The Authors. Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serosurvey of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in livestock, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad, Iran, 2017.J Vector Borne Dis. 2021 Jan-Mar;58(1):70-73. doi: 10.4103/0972-9062.313958. J Vector Borne Dis. 2021. PMID: 34818866
-
Incidence rate and geographic distribution of congenital hypothyroidism in the southwest of Iran (Kohgiluyeh and Boyer Ahmad province) based on geographic information system since 2011-2020.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Nov 30;24(1):790. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05292-y. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39614209 Free PMC article.
-
The Prevalence and Trends of Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, and HIV among Voluntary Blood Donors in Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad Transfusion Center, Southwestern Iran.Iran J Public Health. 2018 Jul;47(7):944-951. Iran J Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30181991 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of gender difference in epidemiology of HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C infections in people with severe mental illness.Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2018 May 4;17:16. doi: 10.1186/s12991-018-0186-2. eCollection 2018. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29755578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coinfection of Schistosoma Species with Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C Viruses.Adv Parasitol. 2016;91:111-231. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2015.12.003. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Adv Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27015949 Review.
References
-
- WHO . Hepatitis, 2023.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

