Predictors of HIV rebound differ by timing of antiretroviral therapy initiation
- PMID: 38329130
- PMCID: PMC10967395
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.173864
Predictors of HIV rebound differ by timing of antiretroviral therapy initiation
Abstract
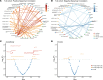
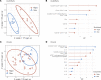
BACKGROUNDIdentifying factors that predict the timing of HIV rebound after treatment interruption will be crucial for designing and evaluating interventions for HIV remission.METHODSWe performed a broad evaluation of viral and immune factors that predict viral rebound (AIDS Clinical Trials Group A5345). Participants initiated antiretroviral therapy (ART) during chronic (N = 33) or early (N = 12) HIV infection with ≥ 2 years of suppressive ART and restarted ART if they had 2 viral loads ≥ 1,000 copies/mL after treatment interruption.RESULTSCompared with chronic-treated participants, early-treated individuals had smaller and fewer transcriptionally active HIV reservoirs. A higher percentage of HIV Gag-specific CD8+ T cell cytotoxic response was associated with lower intact proviral DNA. Predictors of HIV rebound timing differed between early- versus chronic-treated participants, as the strongest reservoir predictor of time to HIV rebound was level of residual viremia in early-treated participants and intact DNA level in chronic-treated individuals. We also identified distinct sets of pre-treatment interruption viral, immune, and inflammatory markers that differentiated participants who had rapid versus slow rebound.CONCLUSIONThe results provide an in-depth overview of the complex interplay of viral, immunologic, and inflammatory predictors of viral rebound and demonstrate that the timing of ART initiation modifies the features of rapid and slow viral rebound.TRIAL REGISTRATIONClinicalTrials.gov NCT03001128FUNDINGNIH National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Merck.
Keywords: AIDS vaccine; AIDS/HIV; Adaptive immunity.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U24 AI143502/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201500017C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069481/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI131385/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007387/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States

