Zirconia CAD-CAM Crowns Behavior after Intraoral Digital Impression in Normal versus Dysfunctional Patients: 3 Years Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38331041
- PMCID: PMC11290922
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0043-1777350
Zirconia CAD-CAM Crowns Behavior after Intraoral Digital Impression in Normal versus Dysfunctional Patients: 3 Years Retrospective Study
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical performance and possible complications of single zirconia crowns fabricated using an intraoral digital computer-aided design-computer-aided manufacturing (CAD-CAM) protocol in normal and dysfunctional patients after 3 years of follow-up.
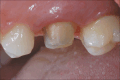
Materials and methods: Seventy patients were included in this study. The teeth were prepared with a knife-edge marginal design, and temporary crowns were placed. Digital impressions were taken using optical scanning, and the frameworks were milled using the same technology. The veneering process was performed by the same dental technician. The occlusal corrections were made before cementation. The outcomes were evaluated in terms of survival, failures, and complications. The marginal adaptation of the crowns was also assessed.
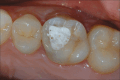
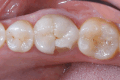
Results: The digital protocol for single zirconia crowns resulted in satisfactory outcomes, with high rates of survival and minimal complications after 3 years of follow-up. The marginal adaptation of the crowns was excellent, with 93% of the restorations achieving the ideal marginal adaptation, while 7% had minor deviations. Parafunctions were found in 41.9% of the prosthetic rehabilitation, but no significant differences were observed between the normal and dysfunctional groups regarding the survival and complications of the crowns.
Conclusion: The digital protocol for single zirconia crowns is a reliable and predictable treatment option, even for patients with parafunction, when proper occlusal corrections are performed before cementation. The use of intraoral digital CAD-CAM technologies with optical impressions can simplify procedures, reduce the workflow time, and minimize the variables linked to the human factor.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Evaluation of fit and efficiency of CAD/CAM fabricated all-ceramic restorations based on direct and indirect digitalization: a double-blinded, randomized clinical trial.Clin Oral Investig. 2016 Mar;20(2):291-300. doi: 10.1007/s00784-015-1504-6. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Clin Oral Investig. 2016. PMID: 26070435 Clinical Trial.
-
Influence of conventional and digital intraoral impressions on the fit of CAD/CAM-fabricated all-ceramic crowns.Clin Oral Investig. 2016 Dec;20(9):2403-2410. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1714-6. Epub 2016 Jan 23. Clin Oral Investig. 2016. PMID: 26800669
-
A Novel Full-Digital Protocol (SCAN-PLAN-MAKE-DONE®) for the Design and Fabrication of Implant-Supported Monolithic Translucent Zirconia Crowns Cemented on Customized Hybrid Abutments: A Retrospective Clinical Study on 25 Patients.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jan 24;16(3):317. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16030317. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30678357 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of marginal and internal fit of lithium disilicate and zirconia all-ceramic CAD-CAM crowns using digital impressions: A systematic review.Prim Dent J. 2023 Mar;12(1):88-95. doi: 10.1177/20501684231154323. Prim Dent J. 2023. PMID: 36916623
-
Marginal Adaptation of CAD/CAM All-Ceramic Crowns Made by Different Impression Methods: A Literature Review.J Prosthodont. 2019 Feb;28(2):e536-e544. doi: 10.1111/jopr.12800. Epub 2018 Apr 20. J Prosthodont. 2019. PMID: 29679423 Review.
Cited by
-
Zirconia in fixed prosthodontics: a review of the literature.Odontology. 2025 Apr;113(2):466-487. doi: 10.1007/s10266-024-01019-8. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Odontology. 2025. PMID: 39508978 Review.
References
-
- Shillingburg H T., Jr Conservative preparations for cast restorations. Dent Clin North Am. 1976;20(02):259–271. - PubMed
-
- Walters R A. A practical irreversible hydrocolloid impression tray holder. J Prosthet Dent. 1990;64(05):625–626. - PubMed
-
- Khajotia S S, Shillingburg H T., Jr Options for posterior ceramic restorations. J Okla Dent Assoc. 1999;90(02):30–34. - PubMed
-
- Levartovsky S, Masri M, Alter E, Pilo R.[Impressions techniques–Part 2] Refuat Hapeh Vehashinayim 199320122933–38., 71 - PubMed
-
- Joda T, Katsoulis J, Bragger U. Clinical fitting and adjustment time for implant-supported crowns comparing digital and conventional workflows. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2016;18(05):946–954. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

