Single-tube four-target lateral flow assay detects human papillomavirus types associated with majority of cervical cancers
- PMID: 38331373
- PMCID: PMC11899860
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2024.115480
Single-tube four-target lateral flow assay detects human papillomavirus types associated with majority of cervical cancers
Abstract
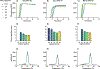
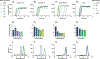
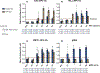
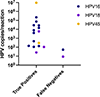
Isothermal nucleic acid amplification methods have many advantages for use at the point of care. However, there is a lack of multiplexed isothermal amplification tests to detect multiple targets in a single reaction, which would be valuable for many diseases, such as infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (hrHPV). In this study, we developed a multiplexed loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) reaction to detect the three most common hrHPV types that cause cervical cancer (HPV16, HPV18, and HPV45) and a cellular control for sample adequacy. First, we characterized the assay limit of detection (LOD) in a real-time reaction with fluorescence readout; after 30 min of amplification the LOD was 100, 10, and 10 copies/reaction of HPV16, HPV18, and HPV45, respectively, and 0.1 ng/reaction of human genomic DNA (gDNA). Next, we implemented the assay on lateral flow strips, and the LOD was maintained for HPV16 and HPV18, but increased to 100 copies/reaction for HPV45 and to 1 ng/reaction for gDNA. Lastly, we used the LAMP test to evaluate total nucleic acid extracted from 38 clinical samples; compared to qPCR, the LAMP test had 89% sensitivity and 95% specificity. When integrated with sample preparation, this multiplexed LAMP assay could be useful for point-of-care testing.
Keywords: HPV; Lateral flow assay; Loop-mediated isothermal amplification; Multiplex.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isothermal Technologies for HPV Detection: Current Trends and Future Perspectives.Pathogens. 2024 Aug 2;13(8):653. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13080653. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39204253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extraction-free RT-RPA assay for detection of HPV16, HPV18, and HPV45 mRNA expression.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;15(1):30450. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13583-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40830554 Free PMC article.
-
One-hour extraction-free loop-mediated isothermal amplification HPV DNA assay for point-of-care testing in Maputo, Mozambique.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 7;16(1):7295. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62454-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40774968 Free PMC article.
-
WarmStart colorimetric LAMP for the specific and rapid detection of HPV16 and HPV18 DNA.J Virol Methods. 2019 Aug;270:87-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2019.04.023. Epub 2019 Apr 28. J Virol Methods. 2019. PMID: 31042552
-
Detection assay for HPV16 and HPV18 by loop‑mediated isothermal amplification with lateral flow dipstick tests.Mol Med Rep. 2017 May;15(5):3203-3209. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6370. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28339040
Cited by
-
Beyond Traditional Lateral Flow Assays: Enhancing Performance Through Multianalytical Strategies.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 23;15(2):68. doi: 10.3390/bios15020068. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39996970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isothermal Technologies for HPV Detection: Current Trends and Future Perspectives.Pathogens. 2024 Aug 2;13(8):653. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13080653. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39204253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extraction-free RT-RPA assay for detection of HPV16, HPV18, and HPV45 mRNA expression.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;15(1):30450. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13583-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40830554 Free PMC article.
-
Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification for Point-of-Care Primary Cervical Cancer Screening.Viruses. 2024 Nov 28;16(12):1852. doi: 10.3390/v16121852. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39772162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One-hour extraction-free loop-mediated isothermal amplification HPV DNA assay for point-of-care testing in Maputo, Mozambique.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 7;16(1):7295. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62454-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40774968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oliveira BB, Veigas B, and Baptista PV, “Isothermal Amplification of Nucleic Acids: The Race for the Next ‘Gold Standard,’” Front. Sens, vol. 2, 2021, Accessed: Sep. 15, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsens.2021.752600 - DOI

