Macromolecular Crowding, Phase Separation, and Homeostasis in the Orchestration of Bacterial Cellular Functions
- PMID: 38331392
- PMCID: PMC10906006
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00622
Macromolecular Crowding, Phase Separation, and Homeostasis in the Orchestration of Bacterial Cellular Functions
Abstract
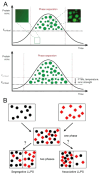
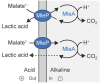
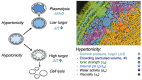
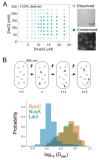
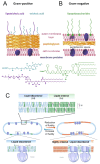
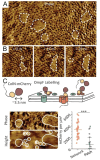
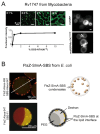
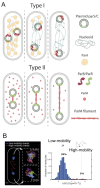
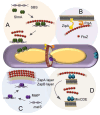
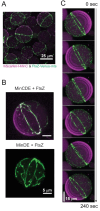
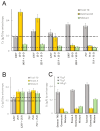
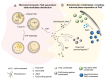
Macromolecular crowding affects the activity of proteins and functional macromolecular complexes in all cells, including bacteria. Crowding, together with physicochemical parameters such as pH, ionic strength, and the energy status, influences the structure of the cytoplasm and thereby indirectly macromolecular function. Notably, crowding also promotes the formation of biomolecular condensates by phase separation, initially identified in eukaryotic cells but more recently discovered to play key functions in bacteria. Bacterial cells require a variety of mechanisms to maintain physicochemical homeostasis, in particular in environments with fluctuating conditions, and the formation of biomolecular condensates is emerging as one such mechanism. In this work, we connect physicochemical homeostasis and macromolecular crowding with the formation and function of biomolecular condensates in the bacterial cell and compare the supramolecular structures found in bacteria with those of eukaryotic cells. We focus on the effects of crowding and phase separation on the control of bacterial chromosome replication, segregation, and cell division, and we discuss the contribution of biomolecular condensates to bacterial cell fitness and adaptation to environmental stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures







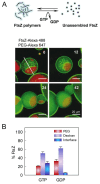
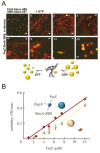
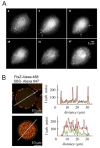
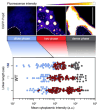

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

