Morin ameliorates myocardial injury in diabetic rats via modulation of inflammatory pathways
- PMID: 38331877
- PMCID: PMC10854036
- DOI: 10.1186/s42826-024-00190-x
Morin ameliorates myocardial injury in diabetic rats via modulation of inflammatory pathways
Abstract
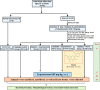
Background: High blood glucose levels in diabetes lead to vascular inflammation which accelerates atherosclerosis. Herein, Morin was orally administered in male Wistar rats, at the dose of 40 mg/kg for 28 days, and on the 27th and 28th day, ISO was administered to designate groups at the dose of 85 mg/kg s.c., to induce myocardial infarction.
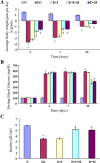
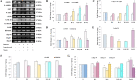
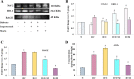
Results: Free radical generation, including ROS, in diabetes following ISO administration, leads to the activation of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of apoptosis. Morin significantly (p ≤ 0.05) reduced oxidative stress (GSH, MDA, SOD), cardiac injury markers (CK-MB, LDH), inflammation (TNF, IL-6), and apoptosis (Bax, BCl2, Caspase-3). In addition, it also reduced insulin and blood glucose levels. Akt/eNOS, Nrf2/HO-1, MAPK signaling pathways, and Insulin signal transduction pathways were positively modulated by morin pre-treatment.
Conclusions: Morin attenuated oxidative stress and inflammation and also modified the activity of various molecular pathways to mitigate cardiomyocyte damage during ISO-induced MI in diabetic rats.
Keywords: Diabetes; Isoproterenol; Molecular signaling pathway; Myocardial necrosis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this publication. The expressed views in this article are of the authors alone.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of MAPK/NF-κB pathway in cardioprotective effect of Morin in isoproterenol induced myocardial injury in rats.Mol Biol Rep. 2019 Feb;46(1):1139-1148. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-04575-9. Epub 2019 Jan 21. Mol Biol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30666500
-
Punicalagin attenuates myocardial oxidative damage, inflammation, and apoptosis in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats: Biochemical, immunohistochemical, and in silico molecular docking studies.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Nov 1;385:110745. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110745. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 37806379
-
Cardioprotective effects of Schisantherin A against isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial infarction through amelioration of oxidative stress and inflammation via modulation of PI3K-AKT/Nrf2/ARE and TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB pathways in rats.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Aug 4;23(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04081-x. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37542250 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of Nrf2/HO-1, caspase-3/Bax/Bcl2 and ATF6/IRE1/PERK/GRP78 signaling pathways in the ameliorative effects of morin against methotrexate-induced testicular toxicity in rats.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Oct;49(10):9641-9649. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07873-5. Epub 2022 Sep 3. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36057755
-
Dapsone Ameliorates Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction via Nrf2/ HO-1; TLR4/ TNF-α Signaling Pathways and the Suppression of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 19;12:669679. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.669679. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34093197 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Acetamiprid-induced testicular toxicity in mice: ameliorative effect and potential mechanisms of morin.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jun 6;25(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04944-5. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40481424 Free PMC article.
-
Morin Mitigates Methamphetamine-Induced Neurotoxicity: Effects on Motor and Cognitive Function.J Exp Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 11;17:307-321. doi: 10.2147/JEP.S498984. eCollection 2025. J Exp Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40524867 Free PMC article.
-
Morin, as a natural flavonoid, provides promising influences against cardiovascular diseases.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;398(6):6293-6310. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03783-4. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39808314
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

