Unraveling the role of the mitochondrial one-carbon pathway in undifferentiated thyroid cancer by multi-omics analyses
- PMID: 38331894
- PMCID: PMC10853200
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45366-0
Unraveling the role of the mitochondrial one-carbon pathway in undifferentiated thyroid cancer by multi-omics analyses
Abstract
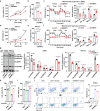
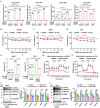
The role of the serine/glycine metabolic pathway (SGP) has recently been demonstrated in tumors; however, the pathological relevance of the SGP in thyroid cancer remains unexplored. Here, we perform metabolomic profiling of 17 tumor-normal pairs; bulk transcriptomics of 263 normal thyroid, 348 papillary, and 21 undifferentiated thyroid cancer samples; and single-cell transcriptomes from 15 cases, showing the impact of mitochondrial one-carbon metabolism in thyroid tumors. High expression of serine hydroxymethyltransferase-2 (SHMT2) and methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2 (MTHFD2) is associated with low thyroid differentiation scores and poor clinical features. A subpopulation of tumor cells with high mitochondrial one-carbon pathway activity is observed in the single-cell dataset. SHMT2 inhibition significantly compromises mitochondrial respiration and decreases cell proliferation and tumor size in vitro and in vivo. Collectively, our results highlight the importance of the mitochondrial one-carbon pathway in undifferentiated thyroid cancer and suggest that SHMT2 is a potent therapeutic target.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Katoh H, Yamashita K, Enomoto T, Watanabe M. Classification and general considerations of thyroid cancer. Ann. Clin. Pathol. 2015;3:1045.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

