A Proof of Concept: Optimized Jawbone-Reduction Model for Mandibular Fracture Surgery
- PMID: 38332406
- PMCID: PMC11574221
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-024-01014-z
A Proof of Concept: Optimized Jawbone-Reduction Model for Mandibular Fracture Surgery
Abstract
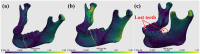
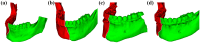
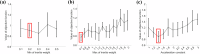
Previous research on computer-assisted jawbone reduction for mandibular fracture surgery has only focused on the relationship between fractured sections disregarding proper dental occlusion with the maxilla. To overcome malocclusion caused by overlooking dental articulation, this study aims to provide a model for jawbone reduction based on dental occlusion. After dental landmarks and fracture sectional features are extracted, the maxilla and two mandible segments are aligned first using the extracted dental landmarks. A swarm-based optimization is subsequently performed by simultaneously observing the fracture section fitting and the dental occlusion condition. The proposed method was evaluated using jawbone data of 12 subjects with simulated and real mandibular fractures. Results showed that the optimized model achieved both accurate jawbone reduction and desired dental occlusion, which may not be possible by existing methods.
Keywords: Computer-assisted surgical planning; Dental occlusion; Jawbone reduction; Mandibular fracture.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- M. Champy, J. P. Loddé, R. Schmitt, J. H. Jaeger, and D. Muster, “Mandibular osteosynthesis by miniature screwed plates via a buccal approach,” J. Maxillofac. Surg., vol. 6, no. C, pp. 14–21, 1978, 10.1016/S0301-0503(78)80062-9. - PubMed
-
- L. Zhao, X. Zhang, Z. Guo, and J. Long, “Use of modified 3D digital surgical guides in the treatment of complex mandibular fractures,” J. Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg., vol. 49, no. 4, pp. 282–291, 2021, 10.1016/j.jcms.2021.01.016. - PubMed
-
- Y. feng Liu, Y. ying Fan, X. feng Jiang, and D. A. Baur, “A customized fixation plate with novel structure designed by topological optimization for mandibular angle fracture based on finite element analysis,” Biomed. Eng. Online, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 1–17, 2017, 10.1186/s12938-017-0422-z. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
