Temporal dynamics and drivers of durable HIV viral load suppression and persistent high- and low-level viraemia during Universal Test and Treat scale-up in Uganda: a population-based study
- PMID: 38332519
- PMCID: PMC10853573
- DOI: 10.1002/jia2.26200
Temporal dynamics and drivers of durable HIV viral load suppression and persistent high- and low-level viraemia during Universal Test and Treat scale-up in Uganda: a population-based study
Abstract
Introduction: Population-level data on durable HIV viral load suppression (VLS) following the implementation of Universal Test and Treat (UTT) in Africa are limited. We assessed trends in durable VLS and viraemia among persons living with HIV in 40 Ugandan communities during the UTT scale-up.
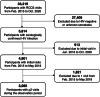
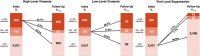
Methods: In 2015-2020, we measured VLS (<200 RNA copies/ml) among participants in the Rakai Community Cohort Study, a longitudinal population-based HIV surveillance cohort in southern Uganda. Persons with unsuppressed viral loads were characterized as having low-level (200-999 copies/ml) or high-level (≥1000 copies/ml) viraemia. Individual virologic outcomes were assessed over two consecutive RCCS survey visits (i.e. visit-pairs; ∼18-month visit intervals) and classified as durable VLS (<200 copies/ml at both visits), new/renewed VLS (<200 copies/ml at follow-up only), viral rebound (<200 copies/ml at initial visit only) or persistent viraemia (≥200 copies/ml at both visits). Population prevalence of each outcome was assessed over calendar time. Community-level prevalence and individual-level predictors of persistent high-level viraemia were also assessed using multivariable Poisson regression with generalized estimating equations.
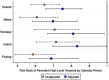
Results: Overall, 3080 participants contributed 4604 visit-pairs over three survey rounds. Most visit-pairs (72.4%) exhibited durable VLS, with few (2.5%) experiencing viral rebound. Among those with any viraemia at the initial visit (23.5%, n = 1083), 46.9% remained viraemic through follow-up, 91.3% of which was high-level viraemia. One-fifth (20.8%) of visit-pairs exhibiting persistent high-level viraemia self-reported antiretroviral therapy (ART) use for ≥12 months. Prevalence of persistent high-level viraemia varied substantially across communities and was significantly elevated among young persons aged 15-29 years (vs. 40- to 49-year-olds; adjusted risk ratio [adjRR] = 2.96; 95% confidence interval [95% CI]: 2.21-3.96), males (vs. females; adjRR = 2.40, 95% CI: 1.87-3.07), persons reporting inconsistent condom use with non-marital/casual partners (vs. persons with marital/permanent partners only; adjRR = 1.38, 95% CI: 1.10-1.74) and persons reporting hazardous alcohol use (adjRR = 1.09, 95% CI: 1.03-1.16). The prevalence of persistent high-level viraemia was highest among males <30 years (32.0%).
Conclusions: Following universal ART provision, most persons living with HIV in south-central Uganda are durably suppressed. Among persons exhibiting any viraemia, nearly half exhibited high-level viraemia for ≥12 months and reported higher-risk behaviours associated with onward HIV transmission. Intensified efforts linking individuals to HIV treatment services could accelerate momentum towards HIV epidemic control.
Keywords: HIV treatment; HIV viraemia; Treat All; antiretroviral therapy; prospective cohort; sub-Saharan Africa.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of the International AIDS Society published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International AIDS Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to disclose.
Figures


Update of
-
Temporal dynamics and drivers of durable HIV viral load suppression and persistent high- and low-level viremia during Universal Test and Treat scale-up in Uganda: a population-based study.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jun 16:2023.06.15.23291445. doi: 10.1101/2023.06.15.23291445. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Int AIDS Soc. 2024 Feb;27(2):e26200. doi: 10.1002/jia2.26200. PMID: 37398460 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS . UNAIDS Data 2021. UNAIDS; 2022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F31DA054849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH105313/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI100031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 75N91019D00024/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI075115/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI123002/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31MH126796/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA054849/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI155080/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143333/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01MH129226/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH129226/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F31 MH126796/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI128779/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI110324/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI102623/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105313/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

