Elucidating common pathogenic transcriptional networks in infective endocarditis and sepsis: integrated insights from biomarker discovery and single-cell RNA sequencing
- PMID: 38332910
- PMCID: PMC10851146
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1298041
Elucidating common pathogenic transcriptional networks in infective endocarditis and sepsis: integrated insights from biomarker discovery and single-cell RNA sequencing
Abstract
Background: Infective Endocarditis (IE) and Sepsis are two closely related infectious diseases, yet their shared pathogenic mechanisms at the transcriptional level remain unclear. This research gap poses a barrier to the development of refined therapeutic strategies and drug innovation.
Methods: This study employed a collaborative approach using both microarray data and single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data to identify biomarkers for IE and Sepsis. It also offered an in-depth analysis of the roles and regulatory patterns of immune cells in these diseases.
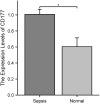
Results: We successfully identified four key biomarkers correlated with IE and Sepsis, namely CD177, IRAK3, RNASE2, and S100A12. Further investigation revealed the central role of Th1 cells, B cells, T cells, and IL-10, among other immune cells and cytokines, in the pathogenesis of these conditions. Notably, the small molecule drug Matrine exhibited potential therapeutic effects by targeting IL-10. Additionally, we discovered two Sepsis subgroups with distinct inflammatory responses and therapeutic strategies, where CD177 demonstrated significant classification value. The reliability of CD177 as a biomarker was further validated through qRT-PCR experiments.
Conclusion: This research not only paves the way for early diagnosis and treatment of IE and Sepsis but also underscores the importance of identifying shared pathogenic mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets at the transcriptional level. Despite limitations in data volume and experimental validation, these preliminary findings add new perspectives to our understanding of these complex diseases.
Keywords: IL-10; immune cells; infective endocarditis; sepsis; single-cell RNA sequencing.
Copyright © 2024 Yi, Zhang, Yang, Chen and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrated multi-omics and artificial intelligence to explore new neutrophils clusters and potential biomarkers in sepsis with experimental validation.Front Immunol. 2024 May 29;15:1377817. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1377817. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38868781 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the immune-metabolic nexus in sepsis: a single-cell sequencing analysis of neutrophil heterogeneity and risk stratification.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 23;15:1398719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1398719. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39108261 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants in genes of the inflammatory response in association with infective endocarditis.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 9;9(10):e110151. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110151. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25299518 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of sepsis.Crit Care Med. 2009 Jul;37(7):2290-8. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a02afc. Crit Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19487943 Review.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing in dissecting microenvironment of age-related macular degeneration: Challenges and perspectives.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Sep;90:102030. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102030. Epub 2023 Aug 5. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 37549871 Review.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing Cardiology through Artificial Intelligence-Big Data from Proactive Prevention to Precise Diagnostics and Cutting-Edge Treatment-A Comprehensive Review of the Past 5 Years.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 May 26;14(11):1103. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14111103. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole blood transcriptomics reveals the enrichment of neutrophil activation pathways during erythema nodosum leprosum reaction.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 23;15:1366125. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1366125. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38715615 Free PMC article.
-
Multidisciplinary Perspectives of Challenges in Infective Endocarditis Complicated by Septic Embolic-Induced Acute Myocardial Infarction.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 May 31;13(6):513. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13060513. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrating bioinformatics and machine learning for comprehensive analysis and validation of diagnostic biomarkers and immune cell infiltration characteristics in pediatric septic shock.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 26;15(1):10456. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95028-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40140612 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

