Preservation versus dissection of the intercostobrachial nerve for breast cancer surgeries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38333310
- PMCID: PMC10849353
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001622
Preservation versus dissection of the intercostobrachial nerve for breast cancer surgeries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: This meta-analysis aimed to compare the efficacy of preservation of the intercostobrachial nerve (ICBN) versus its dissection for patients who underwent breast surgery.
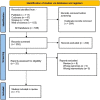
Methods: The authors searched Web of Science, PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, and Scopus from inception until March 2023. Records were screened for eligible studies, and all relevant outcomes were pooled as an odds ratio (OR) with the corresponding 95% CI in the meta-analysis models using RevMan version 5.4.
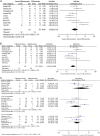
Results: These results from 11 studies (1021 patients) favored preservation of the ICBN over its dissection in terms of anaesthesia and hypaesthesia [OR 0.50, (95% CI, 0.31-0.82); P = 0.006] and [OR 0.33, (95% CI, 0.16-0.68); P = 0.003], respectively. Whereas the overall effect favored ICBN dissection over preservation in the case of hyperaesthesia [OR 4.34, (95% CI, 1.43-13.15); P = 0.01]. Conversely, no significant variance was detected between the two groups in terms of pain [OR 0.68, (95% CI, 0.28-1.61) P = 0.38], paraesthesia [OR 0.88, (95% CI, 0.49-1.60); P = 0.68], and analgesia [OR 1.46, (95% CI, 0.05-45.69); P = 0.83].
Conclusion: This meta-analysis revealed that the preservation of the ICBN has a significant effect on the disturbance of sensory parameters of hypaesthesia and anaesthesia when compared to its dissection. Further studies with larger sample sizes are recommended to precisely compare both techniques on a wider range of parameters.
Keywords: breast cancer; dissection; intercostobrachial nerve; post-mastectomy pain syndrome; preservation.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Intercostobrachial nerve preservation during breast cancer surgery to prevent chronic postsurgical pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2025 Jun 1;51(9):110214. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2025.110214. Online ahead of print. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40472725 Review.
-
Intercostobrachial Nerve (ICBN) Preservation Versus Sacrifice in Axillary Dissection: Randomized Controlled Trial.Am J Clin Oncol. 2021 May 1;44(5):206-209. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000809. Am J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33710131 Clinical Trial.
-
[Functional effects of preserving the intercostobrachial nerve and the lateral thoracic vein during axillary dissection in breast cancer conservative surgery].Vojnosanit Pregl. 2007 Mar;64(3):195-8. doi: 10.2298/vsp0703195i. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2007. PMID: 17438965 Clinical Trial. Serbian.
-
Sensory Changes and Postmastectomy Pain Following Preservation of Intercostobrachial Nerve in Breast Cancer Surgery: a Prospective Randomized Study.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2021 Mar;12(1):108-113. doi: 10.1007/s13193-020-01193-5. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33814840 Free PMC article.
-
Origin, Branching, and Communications of the Intercostobrachial Nerve: a Meta-Analysis with Implications for Mastectomy and Axillary Lymph Node Dissection in Breast Cancer.Cureus. 2017 Mar 17;9(3):e1101. doi: 10.7759/cureus.1101. Cureus. 2017. PMID: 28428928 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Galasso A, Urits I, An D, et al. . A comprehensive review of the treatment and management of myofascial pain syndrome. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2020;24:43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
