Functional balance at rest of hemispheric homologs assessed via normalized compression distance
- PMID: 38333603
- PMCID: PMC10851083
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1261701
Functional balance at rest of hemispheric homologs assessed via normalized compression distance
Abstract
Introduction: The formation and functioning of neural networks hinge critically on the balance between structurally homologous areas in the hemispheres. This balance, reflecting their physiological relationship, is fundamental for learning processes. In our study, we explore this functional homology in the resting state, employing a complexity measure that accounts for the temporal patterns in neurodynamics.
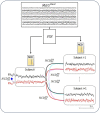
Methods: We used Normalized Compression Distance (NCD) to assess the similarity over time, neurodynamics, of the somatosensory areas associated with hand perception (S1). This assessment was conducted using magnetoencephalography (MEG) in conjunction with Functional Source Separation (FSS). Our primary hypothesis posited that neurodynamic similarity would be more pronounced within individual subjects than across different individuals. Additionally, we investigated whether this similarity is influenced by hemisphere or age at a population level.
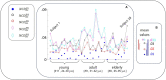
Results: Our findings validate the hypothesis, indicating that NCD is a robust tool for capturing balanced functional homology between hemispheric regions. Notably, we observed a higher degree of neurodynamic similarity in the population within the left hemisphere compared to the right. Also, we found that intra-subject functional homology displayed greater variability in older individuals than in younger ones.
Discussion: Our approach could be instrumental in investigating chronic neurological conditions marked by imbalances in brain activity, such as depression, addiction, fatigue, and epilepsy. It holds potential for aiding in the development of new therapeutic strategies tailored to these complex conditions, though further research is needed to fully realize this potential.
Keywords: functional source separation; neurodynamics; normalized compression distance; resting state; temporal course of the neuronal electrical activity.
Copyright © 2024 Pascarella, Bruni, Armonaite, Porcaro, Conti, Cecconi, Paulon, Vitulano and Tecchio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
-
- Bello J. P. (2011). Measuring structural similarity in music. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19, 2013–2025. doi: 10.1109/TASL.2011.2108287 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

