Genome-wide identification, evolution, and expression analysis of the NAC gene family in chestnut (Castanea mollissima)
- PMID: 38333622
- PMCID: PMC10850246
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1337578
Genome-wide identification, evolution, and expression analysis of the NAC gene family in chestnut (Castanea mollissima)
Abstract
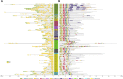
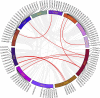
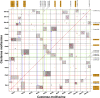
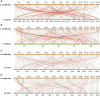
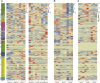
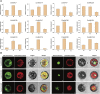
The NAC gene family is one of the most important transcription factor families specific to plants, responsible for regulating many biological processes, including development, stress response, and signal transduction. However, it has not yet been characterized in chestnut, an important nut tree species. Here, we identified 115 CmNAC genes in the chestnut genome, which were divided into 16 subgroups based on the phylogenetic analysis. Numerous cis-acting elements related to auxin, gibberellin, and abscisic acid were identified in the promoter region of CmNACs, suggesting that they play an important role in the growth and development of chestnut. The results of the collinear analysis indicated that dispersed duplication and whole-genome-duplication were the main drivers of CmNAC gene expansion. RNA-seq data of developmental stages of chestnut nut, bud, and ovule revealed the expression patterns of CmNAC genes. Additionally, qRT-PCR experiments were used to verify the expression levels of some CmNAC genes. The comprehensive analysis of the above results revealed that some CmNAC members may be related to chestnut bud and nut development, as well as ovule fertility. The systematic analysis of this study will help to increase understanding of the potential functions of the CmNAC genes in chestnut growth and development.
Keywords: Castanea mollissima; NAC TF; duplication model; evolution; expression patterns.
Copyright © 2024 Cao, Guo, Wang, Wang, Yu, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

