The ever-lasting green tides: What can we do?
- PMID: 38333800
- PMCID: PMC10850537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25220
The ever-lasting green tides: What can we do?
Abstract
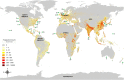
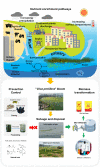
Macroalgal blooms (Green tides) are occurring more frequently in many regions of the world because of the combined effects of increasingly intense human activity and climate change. In the last decade, the world's largest Ulva prolifera green tide has become a recurrent phenomenon, appearing every summer in the southern Yellow Sea, China. Green tides can hurt coastal tourism and eradicate aquaculture and artisanal fishing. Eutrophication in nearshore waters is the ultimate explanation for the explosive growth of the macroalgal biomass, but the specific course of each nearshore green tide is often complex and requires in-depth and extensive research to develop effective mitigation strategies. Researchers have undertaken extensive studies on the prevention, control and mitigation of large-scale green algal blooms, and felicitated the utilization of green tide harmful biomass through bio-refining, bioconversion and other measures. However, due to the large-scale and trans-regional nature of the green tide, the government's administrative coordination measures are also essential for effective control. Nevertheless, it is becoming increasingly urgent to prevent and control the bloom at the early stage, and efficiently salvage and use these valuable raw materials.
Keywords: Developed coastal area; Eutrophication; Green tides.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Cheng-Gang Ren reports administrative support was provided by Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research. Cheng-Gang Ren reports a relationship with Yantai Institute of Coastal Zone Research that includes: employment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Harmful macroalgal blooms (HMBs) in China's coastal water: Green and golden tides.Harmful Algae. 2021 Jul;107:102061. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102061. Epub 2021 Jun 13. Harmful Algae. 2021. PMID: 34456020 Review.
-
Characterization of the development stages and roles of nutrients and other environmental factors in green tides in the Southern Yellow Sea, China.Harmful Algae. 2020 Sep;98:101893. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2020.101893. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Harmful Algae. 2020. PMID: 33129451
-
Integrated biotechnology to mitigate green tides.Environ Pollut. 2022 Sep 15;309:119764. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119764. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Environ Pollut. 2022. PMID: 35841985 Review.
-
Structure-Function Covariation of Phycospheric Microorganisms Associated with the Typical Cross-Regional Harmful Macroalgal Bloom.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Jan 31;89(1):e0181522. doi: 10.1128/aem.01815-22. Epub 2022 Dec 19. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36533927 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention strategies for green tides at source in the Southern Yellow Sea.Mar Pollut Bull. 2022 May;178:113646. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113646. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Mar Pollut Bull. 2022. PMID: 35427815 Review.
References
-
- Wang H., Wang G., Gu W. Macroalgal blooms caused by marine nutrient changes resulting from human activities. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020;57:766–776.
-
- Joniver C.F., Photiades A., Moore P.J., Winters A.L., Woolmer A., Adams J.M. The global problem of nuisance macroalgal blooms and pathways to its use in the circular economy. Algal Res. 2021;58
-
- Brown A.R., Lilley M., Shutler J., Lowe C., Artioli Y., Torres R., Berdalet E., Tyler C.R. Assessing risks and mitigating impacts of harmful algal blooms on mariculture and marine fisheries. Rev. Aquacult. 2020;12:1663–1688.
-
- Liu D., Keesing J.K., He P., Wang Z., Shi Y., Wang Y. The world's largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: formation and implications. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2013;129:2–10.
-
- Guo X., Zhu A., Chen R. China's algal bloom suffocates marine life. Science. 2021;373 751-751. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

