Revolutionizing snakebite care with novel antivenoms: Breakthroughs and barriers
- PMID: 38333815
- PMCID: PMC10850593
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25531
Revolutionizing snakebite care with novel antivenoms: Breakthroughs and barriers
Abstract
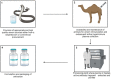
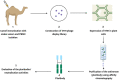
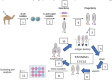
Snakebite envenoming (SBE) is a global public health concern, primarily due to the lack of effective antivenom for treating snakebites inflicted by medically significant venomous snakes prevalent across various geographic locations. The rising demand for safe, cost-effective, and potent snakebite treatments highlights the urgent need to develop alternative therapeutics targeting relevant toxins. This development could provide promising discoveries to create novel recombinant solutions, leveraging human monoclonal antibodies, synthetic peptides and nanobodies. Such technologies as recombinant DNA, peptide and epitope mapping phage display etc) have the potential to exceed the traditional use of equine polyclonal antibodies, which have long been used in antivenom production. Recombinant antivenom can be engineered to target certain toxins that play a critical role in snakebite pathology. This approach has the potential to produce antivenom with improved efficacy and safety profiles. However, there are limitations and challenges associated with these emerging technologies. Therefore, identifying the limitations is critical for overcoming the associated challenges and optimizing the development of recombinant antivenoms. This review is aimed at presenting a thorough overview of diverse technologies used in the development of recombinant antivenom, emphasizing their limitations and offering insights into prospects for advancing recombinant antivenoms.
Keywords: Antibodies; Antivenom; Nanobodies; Recombinant antivenom; Snake venom; Traditional antivenom.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Burbrink F., Pyron R. The taming of the skew: estimating proper confidence intervals for divergence dates. Syst. Biol. 2008;57:317–328. - PubMed
-
- Wallach V., Williams K., Boundy J. first ed. CRC Press; Boca Raton: 2014. Snakes of the World: A Catalogue of Living and Extinct Species.
-
- Casewell N.R., Wuster W., Vonk F.J., Harrison R.A., Fry B.G. Complex cocktails: the evolutionary novelty of venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013;28:219–229. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

