The Impact of ZIF-8 Particle Size Control on Low-Humidity Sensor Performance
- PMID: 38334555
- PMCID: PMC10857053
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14030284
The Impact of ZIF-8 Particle Size Control on Low-Humidity Sensor Performance
Abstract
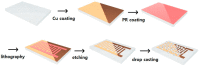
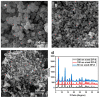
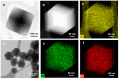
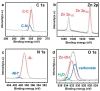
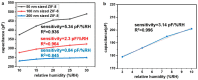
An accurate humidity measurement is essential in various industries, including product stability, pharmaceutical and food preservation, environmental control, and precise humidity management in experiments and industrial processes. Crafting effective humidity sensors through precise material selection is crucial for detecting minute humidity levels across various fields, ultimately enhancing productivity and maintaining product quality. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), particularly zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs), exhibit remarkable properties and offer a wide range of applications in catalysis, sensing, and gas storage due to their structural stability, which resembles zeolites. The previous research on MOF-based humidity sensors have primarily used electrical resistance-based methods. Recently, however, interest has shifted to capacitive-based sensors using MOFs due to the need for humidity sensors at low humidity and the resulting high sensitivity. Nevertheless, further studies are required to optimize particle structure and size. This study analyzes ZIF-8, a stable MOF synthesized in varying particle sizes, to evaluate its performance as a humidity sensor. The structural, chemical, and sensing properties of synthesized ZIF-8 particles ranging from 50 to 200 nanometers were examined through electron microscopy, spectroscopic, and electrochemical analyses. The fabricated copper electrodes combined with these particles demonstrated stable and linear humidity sensing capabilities within the range of 3% to 30% relative humidity (RH).
Keywords: MOF; ZIF-8; capacitive sensor; humidity sensor; particle size.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MOF-Derived Bimetallic CoFe-PBA Composites as Highly Selective and Sensitive Electrochemical Sensors for Hydrogen Peroxide and Nonenzymatic Glucose in Human Serum.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020 Aug 5;12(31):35365-35374. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c09689. Epub 2020 Jul 22. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020. PMID: 32657131
-
Zeolitic imidazolate framework as humidity-resistant solid state-chemiresistive gas sensors: A review.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 15;9(11):e22329. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22329. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38034700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for use in electrochemical and optical chemical sensing and biosensing: a review.Mikrochim Acta. 2020 Mar 16;187(4):234. doi: 10.1007/s00604-020-4173-3. Mikrochim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32180011 Review.
-
The intergrated nanostructure of bimetallic CoNi-based zeolitic imidazolate framework and carbon nanotubes as high-performance electrochemical supercapacitors.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Feb 15;608(Pt 2):1257-1267. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.089. Epub 2021 Oct 24. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 34739989
-
Humidity Sensors Based on Metal-Organic Frameworks.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Nov 26;12(23):4208. doi: 10.3390/nano12234208. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36500831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuzubasoglu B.A. Recent Studies on the Humidity Sensor: A Mini Review. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022;4:4797–4807. doi: 10.1021/acsaelm.2c00721. - DOI
-
- Blank T.A., Eksperiandova L.P., Belikov K.N. Recent trends of ceramic humidity sensors development: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016;228:416–442. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.015. - DOI
-
- Gliszczynska-Swiglo A., Chmielewski J. Electronic Nose as a Tool for Monitoring the Authenticity of Food. A Review. Food Anal. Methods. 2017;10:1800–1816. doi: 10.1007/s12161-016-0739-4. - DOI
-
- Han X., Xia S.S., Cao J., Wang C., Chen M.G. Effect of Humidity on Properties of Lithium-ion Batteries. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021;16:210554. doi: 10.20964/2021.05.54. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

