Intracranial Gene Delivery Mediated by Albumin-Based Nanobubbles and Low-Frequency Ultrasound
- PMID: 38334557
- PMCID: PMC10856598
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14030285
Intracranial Gene Delivery Mediated by Albumin-Based Nanobubbles and Low-Frequency Ultrasound
Abstract
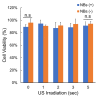
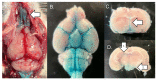
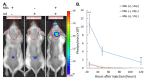
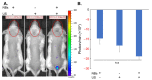
Research in the field of high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) for intracranial gene therapy has greatly progressed over the years. However, limitations of conventional HIFU still remain. That is, genes are required to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in order to reach the neurological disordered lesion. In this study, we introduce a novel direct intracranial gene delivery method, bypassing the BBB using human serum albumin-based nanobubbles (NBs) injected through a less invasive intrathecal route via lumbar puncture, followed by intracranial irradiation with low-frequency ultrasound (LoFreqUS). Focusing on both plasmid DNA (pDNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA), our approach utilizes LoFreqUS for deeper tissue acoustic penetration and enhancing gene transfer efficiency. This drug delivery method could be dubbed as the "Spinal Back-Door Approach", an alternative to the "front door" BBB opening method. Experiments showed that NBs effectively responded to LoFreqUS, significantly improving gene transfer in vitro using U-87 MG cell lines. In vivo experiments in mice demonstrated significantly increased gene expression with pDNA; however, we were unable to obtain conclusive results using mRNA. This novel technique, combining albumin-based NBs and LoFreqUS offers a promising, efficient, targeted, and non-invasive solution for central nervous system gene therapy, potentially transforming the treatment landscape for neurological disorders.
Keywords: central nervous system; drug delivery system; low-frequency ultrasound; nanobubble.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Brain Delivery of Curcumin Through Low-Intensity Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening via Lipid-PLGA Nanobubbles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Nov 4;16:7433-7447. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S327737. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34764649 Free PMC article.
-
Methotrexate-loaded PLGA nanobubbles for ultrasound imaging and Synergistic Targeted therapy of residual tumor during HIFU ablation.Biomaterials. 2014 Jun;35(19):5148-61. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.02.036. Epub 2014 Mar 28. Biomaterials. 2014. PMID: 24680663
-
Influence of Nanobubble Size Distribution on Ultrasound-Mediated Plasmid DNA and Messenger RNA Gene Delivery.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 1;13:855495. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.855495. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35721213 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Intensity MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Mediated Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier for Intracranial Metastatic Diseases.Front Oncol. 2018 Aug 28;8:338. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00338. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30211117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Delivery through Micro/Nanobubble-Assisted Ultrasound.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 22;14(3):480. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030480. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35335857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Progress and potential of nanobubbles for ultrasound-mediated drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2025 Jul;22(7):1007-1030. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2025.2505044. Epub 2025 May 18. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 40353846 Review.
-
Phosphorodiamidate Morpholino Oligomers-Loaded Nanobubbles for Ultrasound-Mediated Delivery to the Myocardium in Muscular Dystrophy.ACS Omega. 2025 Feb 27;10(9):9639-9648. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10896. eCollection 2025 Mar 11. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40092813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arsiwala T.A., Sprowls S.A., Blethen K.E., Adkins C.E., Saralkar P.A., Fladeland R.A., Pentz W., Gabriele A., Kielkowski B., Mehta R.I., et al. Ultrasound-mediated disruption of the blood tumor barrier for improved therapeutic delivery. Neoplasia. 2021;23:676–691. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2021.04.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tachibana K., Kida H. Recent Trends in Application of Encapsulated Ultrafine Bubbles in Medicine. 1st ed. Jenny Stanford Publishing; New York, NY, USA: 2021.
-
- Kida H., Tachibana K. Application of Ultrasound-Responsive Reagents for Drug Delivery Systems. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2023. pp. 181–215. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

