Cellular, Molecular and Clinical Aspects of Aortic Aneurysm-Vascular Physiology and Pathophysiology
- PMID: 38334666
- PMCID: PMC10854611
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13030274
Cellular, Molecular and Clinical Aspects of Aortic Aneurysm-Vascular Physiology and Pathophysiology
Abstract
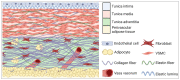
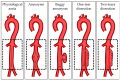
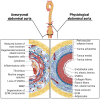
A disturbance of the structure of the aortic wall results in the formation of aortic aneurysm, which is characterized by a significant bulge on the vessel surface that may have consequences, such as distention and finally rupture. Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a major pathological condition because it affects approximately 8% of elderly men and 1.5% of elderly women. The pathogenesis of AAA involves multiple interlocking mechanisms, including inflammation, immune cell activation, protein degradation and cellular malalignments. The expression of inflammatory factors, such as cytokines and chemokines, induce the infiltration of inflammatory cells into the wall of the aorta, including macrophages, natural killer cells (NK cells) and T and B lymphocytes. Protein degradation occurs with a high expression not only of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) but also of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), interferon gamma (IFN-γ) and chymases. The loss of extracellular matrix (ECM) due to cell apoptosis and phenotype switching reduces tissue density and may contribute to AAA. It is important to consider the key mechanisms of initiating and promoting AAA to achieve better preventative and therapeutic outcomes.
Keywords: ECM; VSMCs; inflammation; vessel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Saw S.T., Leong B.D.K., Abdul Aziz D.A. Early Detection of Undiagnosed Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Sub-Aneurysmal Aortic Dilatations in Patients with High-Risk Coronary Artery Disease: The Value of Targetted Screening Programme. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2020;16:215–229. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S250735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koroleva A., Kodenko M., Leonov D., Kulberg N., Lisenko N., Grigorev G., Mokienko O., Vladzymyrskyy A., Morozov S. The Effects of Hidden Aneurysms on the Posterior Flow: Computational Fluid Dynamic Study. Volume 3. Electrical and Power Engineering (REEPE); Moscow, Russia: 2021. pp. 1–4.
-
- Safiri S., Kolahi A.-A., Naghavi M. Global, Regional and National Burden of Bladder Cancer and Its Attributable Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ Glob. Health. 2021;6:e004128. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-004128. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

