Distinct cellular expression and subcellular localization of Kv2 voltage-gated K+ channel subtypes in dorsal root ganglion neurons conserved between mice and humans
- PMID: 38335058
- PMCID: PMC10861167
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.25575
Distinct cellular expression and subcellular localization of Kv2 voltage-gated K+ channel subtypes in dorsal root ganglion neurons conserved between mice and humans
Abstract
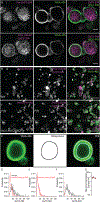
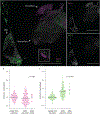
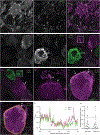
The distinct organization of Kv2 voltage-gated potassium channels on and near the cell body of brain neurons enables their regulation of action potentials and specialized membrane contact sites. Somatosensory neurons have a pseudounipolar morphology and transmit action potentials from peripheral nerve endings through axons that bifurcate to the spinal cord and the cell body within ganglia including the dorsal root ganglia (DRG). Kv2 channels regulate action potentials in somatosensory neurons, yet little is known about where Kv2 channels are located. Here, we define the cellular and subcellular localization of the Kv2 paralogs, Kv2.1 and Kv2.2, in DRG somatosensory neurons with a panel of antibodies, cell markers, and genetically modified mice. We find that relative to spinal cord neurons, DRG neurons have similar levels of detectable Kv2.1 and higher levels of Kv2.2. In older mice, detectable Kv2.2 remains similar, while detectable Kv2.1 decreases. Both Kv2 subtypes adopt clustered subcellular patterns that are distinct from central neurons. Most DRG neurons co-express Kv2.1 and Kv2.2, although neuron subpopulations show preferential expression of Kv2.1 or Kv2.2. We find that Kv2 protein expression and subcellular localization are similar between mouse and human DRG neurons. We conclude that the organization of both Kv2 channels is consistent with physiological roles in the somata and stem axons of DRG neurons. The general prevalence of Kv2.2 in DRG as compared to central neurons and the enrichment of Kv2.2 relative to detectable Kv2.1 in older mice, proprioceptors, and axons suggest more widespread roles for Kv2.2 in DRG neurons.
Keywords: Kv2.1; Kv2.2; dorsal root ganglion; somatosensory neurons; voltage-gated ion channels.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Update of
-
Distinct cellular expression and subcellular localization of Kv2 voltage-gated K+ channel subtypes in dorsal root ganglion neurons conserved between mice and humans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 24:2023.03.01.530679. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.01.530679. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Comp Neurol. 2024 Feb;532(2):e25575. doi: 10.1002/cne.25575. PMID: 38187582 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Distinct cellular expression and subcellular localization of Kv2 voltage-gated K+ channel subtypes in dorsal root ganglion neurons conserved between mice and humans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 24:2023.03.01.530679. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.01.530679. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Comp Neurol. 2024 Feb;532(2):e25575. doi: 10.1002/cne.25575. PMID: 38187582 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Deep Sequencing of Somatosensory Neurons Reveals Molecular Determinants of Intrinsic Physiological Properties.Neuron. 2019 Aug 21;103(4):598-616.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.05.039. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 31248728 Free PMC article.
-
Kv2 dysfunction after peripheral axotomy enhances sensory neuron responsiveness to sustained input.Exp Neurol. 2014 Jan;251:115-26. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.11.011. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24252178 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-gated sodium channels and the molecular pathogenesis of pain: a review.J Rehabil Res Dev. 2000 Sep-Oct;37(5):517-28. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2000. PMID: 11322150 Review.
-
Delta Opioid Receptor Expression and Function in Primary Afferent Somatosensory Neurons.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018;247:87-114. doi: 10.1007/164_2017_58. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28993838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kv2 channels do not function as canonical delayed rectifiers in spinal motoneurons.iScience. 2024 Jul 3;27(8):110444. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110444. eCollection 2024 Aug 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39148717 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Kv2.1 Channels by Kv9.1 Variants.Biomedicines. 2025 May 6;13(5):1119. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051119. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426946 Free PMC article.
-
Sculpting excitable membranes: voltage-gated ion channel delivery and distribution.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2025 Jun;26(6):313-332. doi: 10.1038/s41583-025-00917-2. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40175736 Review.
-
A Kv2 inhibitor combination reveals native neuronal conductances consistent with Kv2/KvS heteromers.Elife. 2025 May 27;13:RP99410. doi: 10.7554/eLife.99410. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40423692 Free PMC article.
-
The Shab family potassium channels are highly enriched at the presynaptic terminals of human neurons.J Biol Chem. 2025 Mar;301(3):108235. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108235. Epub 2025 Jan 27. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39880095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bishop HI, Guan D, Bocksteins E, Parajuli LK, Murray KD, Cobb MM, … Trimmer JS (2015). Distinct cell- and layer-specific expression patterns and independent regulation of Kv2 channel subtypes in cortical pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci, 35(44), 14922–14942. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.1897-15.2015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

