Vascular risk burden is a key player in the early progression of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 38335912
- PMCID: PMC11416150
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2023.12.008
Vascular risk burden is a key player in the early progression of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Understanding whether vascular risk factors (VRFs) synergistically potentiate Alzheimer's disease (AD) progression is important in the context of emerging treatments for preclinical AD. In a group of 503 cognitively unimpaired individuals, we tested whether VRF burden interacts with AD pathophysiology to accelerate neurodegeneration and cognitive decline. Baseline VRF burden was calculated considering medical data and AD pathophysiology was assessed based on cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) amyloid-β1-42 (Aβ1-42) and tau phosphorylated at threonine 181 (p-tau181). Neurodegeneration was assessed with plasma neurofilament light (NfL) and global cognition with the modified version of the Preclinical Alzheimer's Cognitive Composite. The mean (SD) age of participants was 72.9 (6.1) years, and 220 (43.7%) were men. Linear mixed-effects models revealed that an elevated VRF burden synergistically interacted with AD pathophysiology to drive longitudinal plasma NfL increase and cognitive decline. Additionally, VRF burden was not associated with CSF Aβ1-42 or p-tau181 changes over time. Our results suggest that VRF burden and AD pathophysiology are independent processes; however, they synergistically lead to neurodegeneration and cognitive deterioration. In preclinical stages, the combination of therapies targeting VRFs and AD pathophysiology might potentiate treatment outcomes.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Biomarker; Cognitive decline; Neurodegeneration; Vascular risk factor.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests NJA has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Lilly and Quanterix. HZ has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Acumen, Alector, ALZPath, Annexon, Apellis, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Novo Nordisk, Pinteon Therapeutics, Red Abbey Labs, reMYND, Passage Bio, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics, and Wave, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen, and Roche, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. KB has served as a consultant, at advisory boards, or at data monitoring committees for Abcam, Axon, BioArctic, Biogen, JOMDD/Shimadzu, Julius Clinical, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program, all unrelated to the work presented in this paper. SOM reports receiving speaker fees from Medtronic, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Bayer and advisory board fees from Boehringer Ingelheim. PR-N has served on scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Eisai, Novo Nordisk and Roche. ERZ serves on the scientific advisory board of Next Innovative Therapeutics. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
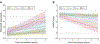
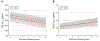
Similar articles
-
Association Between Longitudinal Plasma Neurofilament Light and Neurodegeneration in Patients With Alzheimer Disease.JAMA Neurol. 2019 Jul 1;76(7):791-799. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.0765. JAMA Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31009028 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Associations of Blood Phosphorylated Tau181 and Neurofilament Light Chain With Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer Disease.JAMA Neurol. 2021 Apr 1;78(4):396-406. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.4986. JAMA Neurol. 2021. PMID: 33427873 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma neurofilament light and phosphorylated tau 181 as biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease pathology and clinical disease progression.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021 Mar 25;13(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13195-021-00805-8. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33766131 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of an Alzheimer's Disease Risk-Weighted Polygenic Risk Score for Predicting Rates of Cognitive Decline in Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease: A Prospective Longitudinal Study.J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;66(3):1193-1211. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180713. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018. PMID: 30412495
-
The Associations of Phosphorylated Tau 181 and Tau 231 Levels in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid with Cognitive Function in Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;98(1):13-32. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230799. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38339929
Cited by
-
Impact of the polygenic risk scores for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Feb;21(2):e70003. doi: 10.1002/alz.70003. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 39998851 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors for survival in patients with Alzheimer's disease: a large comprehensive meta-analysis.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Apr 10;14(1):184. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-02897-w. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38600070 Free PMC article.
-
Tau PET positivity predicts clinically relevant cognitive decline driven by Alzheimer's disease compared to comorbid cases; proof of concept in the ADNI study.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Feb;30(2):587-599. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02672-9. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39179903 Free PMC article.
-
Beat-to-beat blood pressure variability, hippocampal atrophy, and memory impairment in older adults.Geroscience. 2025 Feb;47(1):993-1003. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01303-z. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Geroscience. 2025. PMID: 39098984 Free PMC article.
-
Canadian Stroke Best Practice Recommendations: Vascular cognitive impairment, 7th edition practice guidelines update, 2024.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Jan;21(1):e14324. doi: 10.1002/alz.14324. Epub 2025 Jan 16. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 39822128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bangen KJ, Nation DA, Delano-Wood L, Weissberger GH, Hansen LA, Galasko DR, Salmon DP, Bondi MW, 2015. Aggregate effects of vascular risk factors on cerebrovascular changes in autopsy-confirmed Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 11(4), 394–403 e391. doi:10.1016/j.jalz.2013.12.025. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benedet AL, Leuzy A, Pascoal TA, Ashton NJ, Mathotaarachchi S, Savard M, Therriault J, Kang MS, Chamoun M, Scholl M, Zimmer ER, Gauthier S, Labbe A, Zetterberg H, Rosa-Neto P, Blennow K, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging I, 2020. Stage-specific links between plasma neurofilament light and imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 143(12), 3793–3804. doi:10.1093/brain/awaa342. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

