High-fat diet-induced AKT-palmitoylation in hepatocellular carcinoma: a breakthrough mechanistic investigation
- PMID: 38336464
- PMCID: PMC11156549
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-331857
High-fat diet-induced AKT-palmitoylation in hepatocellular carcinoma: a breakthrough mechanistic investigation
Keywords: HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
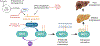
Comment on
-
High-fat diet promotes liver tumorigenesis via palmitoylation and activation of AKT.Gut. 2024 Jun 6;73(7):1156-1168. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2023-330826. Gut. 2024. PMID: 38191266
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Yang WS, Zeng XF, Liu ZN, Zhao QH, Tan YT, Gao J, et al. Diet and liver cancer risk: a narrative review of epidemiological evidence. Br J Nutr 2020;124:330–40. - PubMed
-
- Hernaez R, Peck-Radosavljevic M. MAFLD, HCC and the dilemma of (changing) terminology in liver diseases. Gut 2023;72:9–11. - PubMed
-
- Bu L, Zhang Z, Chen J, Fan Y, Guo J, Su Y, et al. High-fat diet promotes liver tumorigenesis via palmitoylation and activation of AKT. Gut 2024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
