Blood MMP-9 measured at 2 years after lung transplantation as a prognostic biomarker of chronic lung allograft dysfunction
- PMID: 38336710
- PMCID: PMC10858575
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-024-02707-3
Blood MMP-9 measured at 2 years after lung transplantation as a prognostic biomarker of chronic lung allograft dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Long-term outcomes of lung transplantation (LTx) remain hampered by chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD). Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) is a secretory endopeptidase identified as a key mediator in fibrosis processes associated with CLAD. The objective of this study was to investigate whether plasma MMP9 levels may be prognostic of CLAD development.
Methods: Participants were selected from the Cohort in Lung Transplantation (COLT) for which a biocollection was associated. We considered two time points, year 1 (Y1) and year 2 (Y2) post-transplantation, for plasma MMP-9 measurements. We analysed stable recipients at those time points, comparing those who would develop a CLAD within the 2 years following the measurement to those who would remain stable 2 years after.
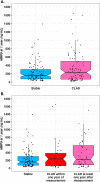
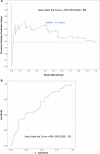
Results: MMP-9 levels at Y1 were not significantly different between the CLAD and stable groups (230 ng/ml vs. 160 ng/ml, p = 0.4). For the Y2 analysis, 129 recipients were included, of whom 50 developed CLAD within 2 years and 79 remained stable within 2 years. MMP-9 plasma median concentrations were higher in recipients who then developed CLAD than in the stable group (230 ng/ml vs. 118 ng/ml, p = 0.003). In the multivariate analysis, the Y2 MMP-9 level was independently associated with CLAD, with an average increase of 150 ng/ml (95% CI [0-253], p = 0.05) compared to that in the stable group. The Y2 ROC curve revealed a discriminating capacity of blood MMP-9 with an area under the curve of 66%.
Conclusion: Plasmatic MMP-9 levels measured 2 years after lung transplantation have prognostic value for CLAD.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AT and BC declare competing interests with Biotest. tSB and RD have ownership interests in the BioMAdvanced Diagnostics company. TV declares competing interests with Boeringer Ingelheim and Mauna Kea. The other authors declare no competing interests. All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form.
Figures

References
-
- Agence de la biomédecine. https://rams.agence-biomedecine.fr/greffe-cardio-pulmonaire-et-pulmonaire-0. Accessed March 14, 2022.
-
- Chambers DC, Zuckermann A, Cherikh WS, et al. The international thoracic organ transplant registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: 37th adult lung transplantation report—2020; focus on deceased donor characteristics. J Heart Lung Transplant Off Publ Int Soc Heart Transplant. 2020;39(10):1016–1027. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2020.07.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

