PLAS-20k: Extended Dataset of Protein-Ligand Affinities from MD Simulations for Machine Learning Applications
- PMID: 38336857
- PMCID: PMC10858175
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-023-02872-y
PLAS-20k: Extended Dataset of Protein-Ligand Affinities from MD Simulations for Machine Learning Applications
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: PLAS-20k: Extended Dataset of Protein-Ligand Affinities from MD Simulations for Machine Learning Applications.Sci Data. 2024 Jul 4;11(1):730. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03585-6. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38965269 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
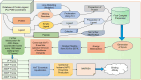
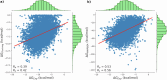
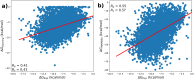
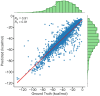
Computing binding affinities is of great importance in drug discovery pipeline and its prediction using advanced machine learning methods still remains a major challenge as the existing datasets and models do not consider the dynamic features of protein-ligand interactions. To this end, we have developed PLAS-20k dataset, an extension of previously developed PLAS-5k, with 97,500 independent simulations on a total of 19,500 different protein-ligand complexes. Our results show good correlation with the available experimental values, performing better than docking scores. This holds true even for a subset of ligands that follows Lipinski's rule, and for diverse clusters of complex structures, thereby highlighting the importance of PLAS-20k dataset in developing new ML models. Along with this, our dataset is also beneficial in classifying strong and weak binders compared to docking. Further, OnionNet model has been retrained on PLAS-20k dataset and is provided as a baseline for the prediction of binding affinities. We believe that large-scale MD-based datasets along with trajectories will form new synergy, paving the way for accelerating drug discovery.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PLAS-5k: Dataset of Protein-Ligand Affinities from Molecular Dynamics for Machine Learning Applications.Sci Data. 2022 Sep 7;9(1):548. doi: 10.1038/s41597-022-01631-9. Sci Data. 2022. PMID: 36071074 Free PMC article.
-
Author Correction: PLAS-20k: Extended Dataset of Protein-Ligand Affinities from MD Simulations for Machine Learning Applications.Sci Data. 2024 Jul 4;11(1):730. doi: 10.1038/s41597-024-03585-6. Sci Data. 2024. PMID: 38965269 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A Comparative Assessment of Predictive Accuracies of Conventional and Machine Learning Scoring Functions for Protein-Ligand Binding Affinity Prediction.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2015 Mar-Apr;12(2):335-47. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2014.2351824. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2015. PMID: 26357221
-
Protein-Ligand Docking in the Machine-Learning Era.Molecules. 2022 Jul 18;27(14):4568. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144568. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine learning approaches and their applications in drug discovery and design.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022 Jul;100(1):136-153. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14057. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022. PMID: 35426249 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence in drug development.Nat Med. 2025 Jan;31(1):45-59. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03434-4. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 39833407 Review.
-
From Static to Dynamic Structures: Improving Binding Affinity Prediction with Graph-Based Deep Learning.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Oct;11(40):e2405404. doi: 10.1002/advs.202405404. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39206846 Free PMC article.
-
MISATO: machine learning dataset of protein-ligand complexes for structure-based drug discovery.Nat Comput Sci. 2024 May;4(5):367-378. doi: 10.1038/s43588-024-00627-2. Epub 2024 May 10. Nat Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 38730184 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Prediction of New Inhibitors for Kirsten Rat Sarcoma G12D Cancer Drug Target Using Machine Learning-Based Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamic Simulation Approaches.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;17(5):551. doi: 10.3390/ph17050551. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794122 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Language Processing Methods for the Study of Protein-Ligand Interactions.J Chem Inf Model. 2025 Mar 10;65(5):2191-2213. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c01907. Epub 2025 Feb 24. J Chem Inf Model. 2025. PMID: 39993834 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

