Immune targeting of HIV-1 reservoir cells: a path to elimination strategies and cure
- PMID: 38337034
- PMCID: PMC11131351
- DOI: 10.1038/s41579-024-01010-8
Immune targeting of HIV-1 reservoir cells: a path to elimination strategies and cure
Abstract
Successful approaches for eradication or cure of HIV-1 infection are likely to include immunological mechanisms, but remarkably little is known about how human immune responses can recognize and interact with the few HIV-1-infected cells that harbour genome-intact viral DNA, persist long term despite antiretroviral therapy and represent the main barrier to a cure. For a long time regarded as being completely shielded from host immune responses due to viral latency, these cells do, on closer examination with single-cell analytic techniques, display discrete footprints of immune selection, implying that human immune responses may be able to effectively engage and target at least some of these cells. The failure to eliminate rebound-competent virally infected cells in the majority of persons likely reflects the evolution of a highly selected pool of reservoir cells that are effectively camouflaged from immune recognition or rely on sophisticated approaches for resisting immune-mediated killing. Understanding the fine-tuned interplay between host immune responses and viral reservoir cells will help to design improved interventions that exploit the immunological vulnerabilities of HIV-1 reservoir cells.
© 2024. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
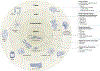

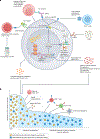
References
-
- UNAIDS. World AIDS Day 2023. UNAIDS; https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/UNAIDS_FactSheet_... (2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AI184094/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI078799/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI155233/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134539/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI164570/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R61 DA047034/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI169768/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI164562/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI135940/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI155171/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R33 DA047034/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI152979/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI176579/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI130005/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI117841/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK120387/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD107670/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI164560/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R33 AI116228/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI116228/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI164566/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

