Influence of the Bracket Material on the Post-Cure Degree of Conversion of Resin-Based Orthodontic Adhesive Systems
- PMID: 38337207
- PMCID: PMC10857419
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16030318
Influence of the Bracket Material on the Post-Cure Degree of Conversion of Resin-Based Orthodontic Adhesive Systems
Abstract
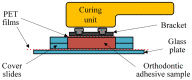
The aim of this study was to examine the influence of the orthodontic bracket material on the short-term and long-term post-cure development of the degree of conversion (DC) of resin-based orthodontic adhesive systems. Five commercially available materials characterized by different compositions and curing modes (light-curable or dual-curable) were tested under three different light curing conditions: without brackets (control group, CO), and in the presence of metal brackets (MB group) or ceramic brackets (CB group). Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy was used to determine the post-cure DC development, both after "short-term" periods (2, 6, and 10 min) and "long-term" periods (1, 7, and 28 days). The short-term DC values ranged from 43.9% to 76.1%, and the long-term DC values were higher and ranged from 54.3% to 85.3%. The MB group demonstrated significantly lower short-term DC values compared to the CO and the CB groups, while the CB group had statistically similar or slightly lower DC values compared to the CO group. Long-term DC values in the MB and the CB groups were statistically lower or similar compared to the CO group, which depended on the post-cure time. The results indicated that the post-cure DC development was highly material-dependent and affected by the presence of different types of bracket material.
Keywords: FTIR; degree of conversion; orthodontic adhesive systems; orthodontic brackets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Rahiotis C. Degree of Cure and Monomer Leaching from Orthodontic Adhesive Resins: In Vitro and in Vivo Evidence. Semin. Orthod. 2010;16:266–273. doi: 10.1053/j.sodo.2010.06.007. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

