Electrochemical Analysis of Curcumin in Real Samples Using Intelligent Materials
- PMID: 38337251
- PMCID: PMC10857161
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16030366
Electrochemical Analysis of Curcumin in Real Samples Using Intelligent Materials
Abstract
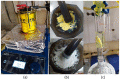
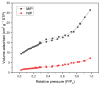
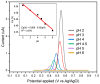
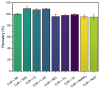
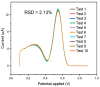
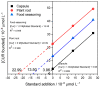
Curcumin is a compound of great importance in the food industry due to its biological and pharmacological properties, which include being an antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, and anticarcinogenic. This paper proposes the synthesis of an electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) and MWCNT by drop casting deposited on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) for the selective quantification of curcumin in food samples. The synthesized compounds are characterized by Fourier transform infrared (IR), Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET), and electrochemical techniques such as cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV). The optimal conditions for further experiments were determined by selecting these parameters. We examined three food products, commercial capsules, turmeric rhizomes, and commercial turmeric powder, employing both electrochemical and HPLC methods for the analysis. The electrochemical method revealed a limit of detection (LOD) value of 0.1365 µmol L-1, compared with the HPLC analysis, which gave a value of 3.55 µmol L-1. Furthermore, the MIP material demonstrated superior selectivity for the analyte compared to potential interferents. The recovery percentage, determined using the HPLC method, fell within the range of 87.5% to 102.6.
Keywords: curcumin; electrochemical sensor; molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Metal-organic framework-based molecularly imprinted polymer as a high sensitive and selective hybrid for the determination of dopamine in injections and human serum samples.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Oct 30;118:129-136. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.07.047. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 30075383
-
Sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of bisphenol A based on SBA-15 like Cu-PMO modified glassy carbon electrode.Food Chem. 2021 Oct 1;358:129763. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129763. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 34000688
-
[Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers based on covalent organic frameworks and their application to selective recognition of trace norfloxacin in milk].Se Pu. 2022 Jan;40(1):1-9. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2021.03013. Se Pu. 2022. PMID: 34985210 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Rapid and Selective Detection of Hypoxanthine.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 12;12(12):1157. doi: 10.3390/bios12121157. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551124 Free PMC article.
-
Enantioselective recognition of esomeprazole with a molecularly imprinted sol-gel-based electrochemical sensor.Mikrochim Acta. 2022 May 19;189(6):225. doi: 10.1007/s00604-022-05321-6. Mikrochim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35585299
Cited by
-
Curcumin Electroanalysis at a Disposable Graphite Electrode.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Feb 23;15(3):137. doi: 10.3390/bios15030137. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40136935 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarado H.-L., Limón D., Calpena-Campmany A.-C., Mallandrich M., Rodríguez-Cid L., Aliaga-Alcalde N., González-Campo A., Pérez-García L. Intrinsic Permeation and Anti-Inflammatory Evaluation of Curcumin, Bisdemethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethylcurcumin by a Validated HPLC-UV Method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24:6640. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076640. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Kader M.S., Salkini A.A., Alam P., Alshahrani K.A., Foudah A.I., Alqarni M.H. A High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatographic Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Curcumin I, Curcumin II and Curcumin III in Curcuma longa and Herbal Formulation. Separations. 2022;9:94. doi: 10.3390/separations9040094. - DOI
-
- Rios-Aguirre S., Gil-Garzón M.A. Microencapsulación por secado por aspersión de compuestos bioactivos en diversas matrices: Una revisión. TecnoLógicas. 2021;24:e1836. doi: 10.22430/22565337.1836. - DOI
-
- Gupta S., Babu B.V. Removal of toxic metal Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using sawdust as adsorbent: Equilibrium, kinetics and regeneration studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2009;150:352–365. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.01.013. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

