Polyelectrolyte-Surfactant Complex Nanofibrous Membranes for Antibacterial Applications
- PMID: 38337304
- PMCID: PMC10857514
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16030414
Polyelectrolyte-Surfactant Complex Nanofibrous Membranes for Antibacterial Applications
Abstract
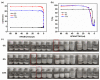
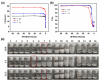
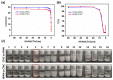
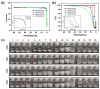
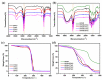
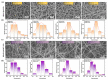
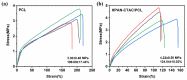
Polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes (PESCs) have garnered significant attention due to their extensive range of biological and industrial applications. Most present applications are predominantly used in liquid or emulsion states, which limits their efficacy in solid material-based applications. Herein, pre-hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile (HPAN) and quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) are employed to produce PESC electrospun membranes via electrospinning. The formation process of PESCs in a solution is observed. The results show that the degree of PAN hydrolysis and the varying alkyl chain lengths of surfactants affect the rate of PESC formation. Moreover, PESCs/PCL hybrid electrospun membranes are fabricated, and their antibacterial activities against both Gram-negative Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) are investigated. The resulting electrospun membranes exhibit high bactericidal efficacy, which enables them to serve as candidates for future biomedical and filtration applications.
Keywords: antibacterial; hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile; polyelectrolyte; quaternary ammonium salt; surfactant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
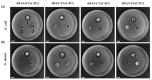
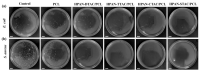
Similar articles
-
Electrospun nanofibers of polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes for antibacterial wound dressing application.Soft Matter. 2019 Dec 11;15(48):10020-10028. doi: 10.1039/c9sm02043h. Soft Matter. 2019. PMID: 31763659
-
Long-term, synergistic and high-efficient antibacterial polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membrane prepared by "one-pot" electrospinning process.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022 Mar;609:718-733. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.11.075. Epub 2021 Nov 18. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022. PMID: 34863546
-
Long-acting and broad-spectrum antimicrobial electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone)/gelatin micro/nanofibers for wound dressing.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018 Jan 1;509:275-284. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.08.092. Epub 2017 Sep 1. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2018. PMID: 28915485
-
Polyelectrolyte-Surfactant Complexes As a Formulation Tool for Drug Delivery.Langmuir. 2022 Nov 8;38(44):13330-13343. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c02166. Epub 2022 Oct 24. Langmuir. 2022. PMID: 36278880 Review.
-
Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes for Controlling Airborne Viruses: Present Status, Standardization of Aerosol Filtration Tests, and Future Development.ACS Environ Au. 2022 Jul 20;2(4):290-309. doi: 10.1021/acsenvironau.1c00047. Epub 2022 Mar 11. ACS Environ Au. 2022. PMID: 35928556 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ionic self-assembly of redox-active polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes: mesostructured soft materials for electrochemical nanoarchitectonics.Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2025 Apr 29;26(1):2497309. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2025.2497309. eCollection 2025. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2025. PMID: 40458735 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Madinya J.J., Tjo H., Meng X., Ramírez Marrero I.A., Sing C.E., Perry S.L. Surface Charge Density and Steric Repulsion in Polyelectrolyte–Surfactant Coacervation. Macromolecules. 2023;11:3973–3988. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.3c00464. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

