Wastewater Treatment Using Membrane Bioreactor Technologies: Removal of Phenolic Contaminants from Oil and Coal Refineries and Pharmaceutical Industries
- PMID: 38337332
- PMCID: PMC10857039
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16030443
Wastewater Treatment Using Membrane Bioreactor Technologies: Removal of Phenolic Contaminants from Oil and Coal Refineries and Pharmaceutical Industries
Abstract
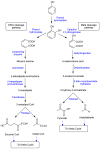
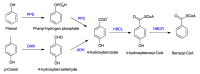
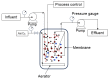
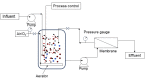
Huge amounts of noxious chemicals from coal and petrochemical refineries and pharmaceutical industries are released into water bodies. These chemicals are highly toxic and cause adverse effects on both aquatic and terrestrial life. The removal of hazardous contaminants from industrial effluents is expensive and environmentally driven. The majority of the technologies applied nowadays for the removal of phenols and other contaminants are based on physio-chemical processes such as solvent extraction, chemical precipitation, and adsorption. The removal efficiency of toxic chemicals, especially phenols, is low with these technologies when the concentrations are very low. Furthermore, the major drawbacks of these technologies are the high operation costs and inadequate selectivity. To overcome these limitations, researchers are applying biological and membrane technologies together, which are gaining more attention because of their ease of use, high selectivity, and effectiveness. In the present review, the microbial degradation of phenolics in combination with intensified membrane bioreactors (MBRs) has been discussed. Important factors, including the origin and mode of phenols' biodegradation as well as the characteristics of the membrane bioreactors for the optimal removal of phenolic contaminants from industrial effluents are considered. The modifications of MBRs for the removal of phenols from various wastewater sources have also been addressed in this review article. The economic analysis on the cost and benefits of MBR technology compared with conventional wastewater treatments is discussed extensively.
Keywords: contaminants removal; human health; industrial effluents; membrane bioreactor; phenolics; sustainability; wastewater treatment; water pollution.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Zoheb Karim was employed by the company MoRe Research Örnsköldsvik AB. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
State-of-the-Art Review on the Application of Membrane Bioreactors for Molecular Micro-Contaminant Removal from Aquatic Environment.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Apr 15;12(4):429. doi: 10.3390/membranes12040429. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biodegradation of phenolic mixtures in a sequencing batch reactor. A kinetic study.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2008 May;15(3):188-95. doi: 10.1065/espr2007.12.470. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2008. PMID: 18504836
-
Removal of trace organic contaminants from domestic wastewater: A meta-analysis comparison of sewage treatment technologies.Environ Int. 2016 Jul-Aug;92-93:183-8. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.03.031. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Environ Int. 2016. PMID: 27107223 Review.
-
Bioremediation of industrial effluents: A synergistic approach.J Basic Microbiol. 2022 Mar;62(3-4):395-414. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202100225. Epub 2021 Sep 13. J Basic Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34516028 Review.
Cited by
-
Response surface methodology to investigate the effects of operational parameters on membrane bioreactor.Water Sci Technol. 2025 Mar;91(5):453-468. doi: 10.2166/wst.2025.031. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Water Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40087959
References
-
- Hou S.Y., Zhao X., Liu Y., Tillotson M.R., Weng S.L., Wang H., Li Y.P., Liu B.Y., Feng K.S., Zhang N. Spatial analysis connects excess water pollution discharge, industrial production, and consumption at the sectoral level. Npj Clean Water. 2022;5:4. doi: 10.1038/s41545-022-00152-7. - DOI
-
- Haseena M., Malik M.F., Javed A., Arshad S., Asif N., Zulfiqar S., Hanif J. Water pollution and human health. Environ. Risk Assess. Remediat. 2017;1:16–19. doi: 10.4066/2529-8046.100020. - DOI
-
- Takht Ravanchi M., Kaghazchi T., Kargari A. Application of membrane separation processes in petrochemical industry: A review. Desalination. 2009;235:199–244. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2007.10.042. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- Fundamental Fund: fiscal year 2023/National Science Research and Innovation Fund (NSRF)
- N42A650248/National Research Council of Thailand
- 2023 International Postdoctoral Fellowship Award from International Relations Affair/Mahidol University
- Scholarship for Ph.D. students 2022/Mahidol University
- 108-2638-E-002-003-MY2/Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), Taiwan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

