How Reliable Is Breast Volume Assessment When the Patient Is Lying Flat?-Volumetric Assessment of Breast Volume Using a Vectra H2 Handheld Device in Different Positions
- PMID: 38337404
- PMCID: PMC10856139
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13030709
How Reliable Is Breast Volume Assessment When the Patient Is Lying Flat?-Volumetric Assessment of Breast Volume Using a Vectra H2 Handheld Device in Different Positions
Abstract
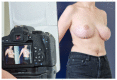
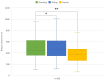
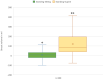
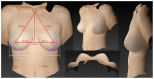
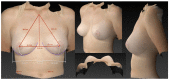
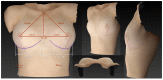
(1) Background: Three-dimensional (3D) volumetric assessment is receiving increased recognition in breast surgery. It is commonly used for preoperative planning and postoperative control with the patient standing in an upright position. Recently, intraoperative use was evaluated with patients in the supine position. The aim of this prospective study was to evaluate the volumetric changes in 3D surface imaging depending on the patient's position. (2) Methods: 3D volumetric analysis was performed using a Vectra-H2 device with patients in standing, sitting, and supine positions. A total of 100 complete datasets of female breasts were included in the study. The measured volumes of each evaluated breast (n = 200) were compared between the three positions. (3) Results: The mean difference between the 3D volumetric assessments of the sitting and standing positions per breast was 7.15 cc and, thus, statistically insignificant (p = 0.28). However, the difference between supine and standing positions, at 120.31 cc, was significant (p < 0.01). (4) Conclusions: The 3D volumetric assessment of breasts in the supine position did not statistically correlate with the validated assessment of breast volume in the standing position while breast volume in the sitting position is reliable and correlates with the assessment of a standing patient. We conclude that intraoperative volumetric assessment should be performed with patients in an upright sitting position.
Keywords: 3-D volumetric assessment; Vectra; Vectra H2 handheld device; breast operation; breast volume; breast volumetry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest regarding the research, authorship, and publication of this article. The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Munir A., Huws A.M., Khawaja S., Khan S., Holt S., Sharaiha Y. Automated Breast Volume Assessment Derived From Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Images Compared to Mastectomy Specimen Weight and Its Applications in Cosmetic Optimisation. Cureus. 2021;13:e19642. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19642. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

