Right Ventricular Function in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy: Potential Value of Strain Echocardiography
- PMID: 38337410
- PMCID: PMC10856386
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13030717
Right Ventricular Function in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy: Potential Value of Strain Echocardiography
Abstract
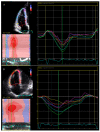
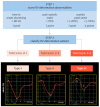
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy is an inherited cardiomyopathy, characterized by abnormal cell adhesions, disrupted intercellular signaling, and fibrofatty replacement of the myocardium. These changes serve as a substrate for ventricular arrhythmias, placing patients at risk of sudden cardiac death, even in the early stages of the disease. Current echocardiographic criteria for diagnosing arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy lack sensitivity, but novel markers of cardiac deformation are not subject to the same technical limitations as current guideline-recommended measures. Measuring cardiac deformation using speckle tracking allows for meticulous quantification of global systolic function, regional function, and dyssynchronous contraction. Consequently, speckle tracking to quantify myocardial strain could potentially be useful in the diagnostic process for the determination of disease progression and to assist risk stratification for ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. This narrative review provides an overview of the potential use of different myocardial right ventricular strain measures for characterizing right ventricular dysfunction in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy and its utility in assessing the risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
Keywords: ARVC; arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy; right ventricle; speckle tracking; strain.
Conflict of interest statement
C.L.B.: none; T.B.-S.: research grants from Sanofi Pasteur, GSK, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, Boston Scientific, and GE Healthcare; consulting fees from Novo Nordisk, IQVIA, Parexel, Amgen, CSL Seqirus, GSK, and Sanofi Pasteur; and lecture fees from Bayer, Novartis, Sanofi Pasteur, GE Healthcare, and GSK. K.G.S.: advisory board member at Sanofi Pasteur. M.S.: none. M.C.H.L.: none. N.D.J.: none. F.J.O.: none. The organizations had no role in any part of this review.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

