Wernicke Syndrome: Case Report and Literature Review of Contributing Factors-Can Malpractice Dynamics Be Identified?
- PMID: 38337411
- PMCID: PMC10856512
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13030716
Wernicke Syndrome: Case Report and Literature Review of Contributing Factors-Can Malpractice Dynamics Be Identified?
Abstract
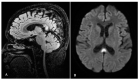
Wernicke Encephalopathy (WE) is a neurological acute syndrome related to vitamin B1 deficiency and is relatively common in patients with chronic alcoholism. In the case of Hyperemesis Gravidarum, thiamine body stores become unable to meet the increased demand, resulting in acute deficiency. WE is associated with typical clinical and radiological findings. Treatment pathways rely on thiamine replacement. The case herein reported is centered around a 33-year-old diabetic patient at 12 weeks of gestation, with WE due to hyperemesis gravidarum. The disease manifested itself with weakness, mental confusion, headache, and impaired vision. The diagnosis was established after the detection of typical findings by MRI. Thirty days after therapy was started, most of the patient's neurological disorders were resolved. The patient was discharged 40 days later with instructions to continue daily thiamine supplementation. The pregnancy outcome was good. Unfortunately, mild ataxia persisted in 2-year follow-up as a long-term consequence. When diagnosed and treated, WE has a favorable prognosis. However, roughly 80% of patients experience memory loss, which may continue for a long time, while gait disorders reportedly affect about 35% of patients. Mild ataxia and dysmetria may persist, too. We reviewed the scientific literature on WE in women with HG until February 2023. Hardly any authors report data on long-term sequelae. Our report emphasizes how important it is to take into consideration this complication in clinical practice, referring to published guidelines and recommendations. Neurological maternal sequelae can demonstrably persist despite early diagnosis and appropriate management. For this reason, a long-term follow-up is recommended. Wernicke syndrome management cannot yet rely on well-established conclusive guidelines; hence, a cautionary approach ought to be prioritized in order to ensure medicolegal soundness.
Keywords: Hyperemesis Gravidarum (HG); Wernicke encephalopathy (WE); ataxia; guidelines; medicolegal standards; thiamine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wernicke Encephalopathy as a Complication of Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Case Report.Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020 Oct;42(10):672-675. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1714721. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020. PMID: 33129223 English.
-
Atypical neurological manifestations in Wernicke's encephalopathy due to hyperemesis gravidarum.Nutr Neurosci. 2022 Oct;25(10):2051-2056. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2021.1931781. Epub 2021 May 27. Nutr Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34042559
-
Fetal demise and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome in a patient with hyperemesis gravidarum: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2023 Feb 2;17(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13256-022-03748-2. J Med Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36726136 Free PMC article.
-
Wernicke's encephalopathy in women with hyperemesis gravidarum - Case series and literature review.Trop Doct. 2022 Jan;52(1):98-100. doi: 10.1177/00494755211014396. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Trop Doct. 2022. PMID: 34167385 Review.
-
Hyperemesis gravidarum complicated by Wernicke encephalopathy: background, case report, and review of the literature.Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2006 Apr;61(4):255-68. doi: 10.1097/01.ogx.0000206336.08794.65. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2006. PMID: 16551377 Review.
Cited by
-
[Differential diagnosis of acute onset loss of consciousness : A case-based review for the radiologist and neurologist].Radiologie (Heidelb). 2025 Aug;65(8):601-606. doi: 10.1007/s00117-025-01475-5. Epub 2025 Jun 29. Radiologie (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40583057 German. No abstract available.
-
Wernicke encephalopathy in pregnancy associated with hyperemesis gravidarum: a case report.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025 Jul 3;25(1):720. doi: 10.1186/s12884-025-07830-7. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2025. PMID: 40610948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomson A.D., Cook C.C.H., Guerrini I., Sheedy D., Harper C., Marshall E.J. Review * Wernicke’s Encephalopathy Revisited * Translation of the Case History Section of the Original Manuscript by Carl Wernicke “Lehrbuch Der Gehirnkrankheiten Fur Aerzte and Studirende” (1881) with a Commentary. Alcohol. Alcohol. 2008;43:174–179. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agm144. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Whitfield K.C., Bourassa M.W., Adamolekun B., Bergeron G., Bettendorff L., Brown K.H., Cox L., Fattal-Valevski A., Fischer P.R., Frank E.L., et al. Thiamine Deficiency Disorders: Diagnosis, Prevalence, and a Roadmap for Global Control Programs. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018;1430:3–43. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13919. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources