Comparison of the Effects of Anaesthesia Methods Used in Caesarean Delivery on Neonatal Cerebral and Renal Oxygenation: A Randomised Controlled Trial
- PMID: 38337566
- PMCID: PMC10856314
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13030873
Comparison of the Effects of Anaesthesia Methods Used in Caesarean Delivery on Neonatal Cerebral and Renal Oxygenation: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
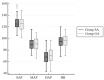
Background: During a newborn's adaptation to extrauterine life, many changes take place that are influenced by various factors. The type of delivery and anaesthesia strategy utilised during labour can modify these adaptive modifications. In this regard, this study was designed to compare the effects of general and spinal anaesthesia on cerebral and renal oxygenation after elective caesarean deliveries. Methods: This randomised controlled study comprised sixty parturient women who were over 18 years old and had a gestational age between 37 and 41 weeks. All participants had an ASA (American Society of Anesthesiologists) classification of II. Neonatal cerebral (CrSO2) and renal (RrSO2) regional oxygen saturations were assessed using near-infrared spectroscopy. Additionally, the 1st-5th min Apgar scores, preductal and postductal peripheral oxygen saturation (SpO2), and perfusion index were recorded in both the general anaesthesia and spinal anaesthesia groups. Results: There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of CrSO2 or RrSO2 values. The values of CrSO2 and RrSO2 in both groups showed a significant rise from the 10th to the 15th min, respectively. Conclusions: General and spinal anaesthesia techniques used for cesarean delivery have similar effects on neonatal cerebral and renal oxygenation.
Keywords: anaesthesia; near-infrared spectroscopy; newborn; regional oxygen saturation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cerebral Oxygenation in Neonates Immediately after Cesarean Section and Mode of Maternal Anesthesia.Neonatology. 2019;116(2):132-139. doi: 10.1159/000499046. Epub 2019 May 16. Neonatology. 2019. PMID: 31096224
-
Cerebral, renal and mesenteric regional oxygen saturation of term infants during transition.J Pediatr Surg. 2015 Aug;50(8):1273-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2015.04.004. Epub 2015 Apr 15. J Pediatr Surg. 2015. PMID: 25933924
-
Cesarean under general or epidural anesthesia: does it differ in terms of regional cerebral oxygenation?Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2014 Dec;52(4):159-62. doi: 10.1016/j.aat.2014.09.002. Epub 2014 Nov 7. Acta Anaesthesiol Taiwan. 2014. PMID: 25446195
-
Combined spinal-epidural versus spinal anaesthesia for caesarean section.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 10;10(10):CD008100. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008100.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31600820 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of intravenous dexmedetomidine and remifentanil on neonatal outcomes after caesarean section under general anaesthesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2021 Oct 1;38(10):1085-1095. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000001558. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2021. PMID: 34101715
Cited by
-
The use of near-infrared spectroscopy to measure kidney oxygenation in the neonatal intensive care unit.Pediatr Nephrol. 2025 May 16. doi: 10.1007/s00467-025-06792-4. Online ahead of print. Pediatr Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40379984
References
-
- Saygi A.I., Ozdamar O., Gun I., Emirkadı H., Müngen E., Akpak Y.K. Comparison of maternal and fetal outcomes among patients undergoing caesarean section under general and spinal anesthesia: A randomized clinical trial. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2015;133:227–234. doi: 10.1590/1516-3180.2014.8901012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bailey S.M., Hendricks-Munoz K.D., Mally P. Cerebral, renal, and splanchnic tissue oxygen saturation values in healthy term newborns. Am. J. Perinatol. 2014;31:339–344. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

