From Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Out with the Old, in with the New
- PMID: 38337575
- PMCID: PMC10856125
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13030880
From Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Out with the Old, in with the New
Abstract
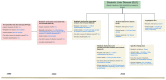
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease (CLD) affecting a quarter of the global population [...].
Conflict of interest statement
H.D.T. has consulted for Novo Nordisk. MN Advisory Board: Altimmune, BI, Cytodyn, Corcept, 89BIO, GSK, Madrigal, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Northsea therapeutics, Terns, and Takeda. Principal Investigator for a Drug Study: Allergan, Akero, BMS, BI, Gilead, Galectin, Genfit, GSK, Conatus, Corcept, Enanta, Madrigal, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Shire, Takeda, Terns, Viking and Zydus. Stockholder: Rivus Pharma, CIMA, Cytodyn, and ChronWell.
Figures
References
-
- Noureddin M., Vipani A., Bresee C., Todo T., Kim I.K., Alkhouri N., Setiawan V.W., Tran T., Ayoub W.S., Lu S.C., et al. NASH Leading Cause of Liver Transplant in Women: Updated Analysis of Indications For Liver Transplant and Ethnic and Gender Variances. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018;113:1649–1659. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0088-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eslam M., Newsome P.N., Sarin S.K., Anstee Q.M., Targher G., Romero-Gomez M., Zelber-Sagi S., Wai-Sun Wong V., Dufour J.-F., Schattenberg J.M., et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020;73:202–209. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.03.039. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

