Characteristics of Functional Hyperthermia Detected in an Outpatient Clinic for Fever of Unknown Origin
- PMID: 38337583
- PMCID: PMC10856695
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13030889
Characteristics of Functional Hyperthermia Detected in an Outpatient Clinic for Fever of Unknown Origin
Abstract
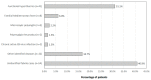
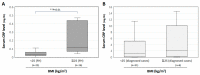
Background: Functional hyperthermia (FH) is characterized by hyperthermia resulting from sympathetic hyperactivity rather than inflammation, and it is frequently overlooked by medical practitioners due to the absence of abnormalities in a medical examination. Although FH is an important differential diagnosis for fever of unknown origin (FUO), the literature on FUO cases in Japan lacks information on FH. In this study, we aimed to uncover the population of FH patients hidden in FUO cases. Methods: An outpatient clinic for FUO was established at Okayama University Hospital, and 132 patients were examined during the period from May 2019 to February 2022. Results: A diagnosis of FH was made in 31.1% of the FUO cases, and FH predominantly affected individuals in their third and fourth decades of life with a higher incidence in females (68.3%). The frequency of a history of psychiatric illness was higher in patients with FH than in patients with other febrile illnesses. Although the C-reactive protein (CRP) is generally negative in FH cases, some obese patients, with a body mass index ≥ 25 had slightly elevated levels of CRP but were diagnosed with FH. Conclusions: The results showed the importance of identifying FH when encountering patients with FUO without any organic etiology.
Keywords: C-reactive protein (CRP); fever of unknown origin (FUO); functional hyperthermia (FH); psychiatric disorder; psychogenic fever.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Oka T. Stress-induced hyperthermia and hypothermia. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018;157:599–621. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

