Lactose Intolerance versus Cow's Milk Allergy in Infants: A Clinical Dilemma
- PMID: 38337698
- PMCID: PMC10856892
- DOI: 10.3390/nu16030414
Lactose Intolerance versus Cow's Milk Allergy in Infants: A Clinical Dilemma
Abstract
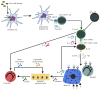
Due to its very early introduction, cow's milk is one of the first foods that can cause adverse reactions in human beings. Lactose intolerance (LI) and cow's milk allergy (CMA) are the most common adverse reactions to cow's milk. While LI is due to insufficient small intestinal lactase activity and/or a large quantity of ingested lactose, CMA is an aberrant immune reaction to cow's milk proteins, particularly casein or β-lactoglobulin. However, the clinical manifestations of LI and CMA, particularly their gastrointestinal signs and symptoms, are very similar, which might lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis as well as nutritional risks due to inappropriate dietary interventions or unnecessary dietary restriction. Formula-fed infants with LI should be treated with formula with reduced or no lactose, while those with CMA should be treated with formula containing extensive hydrolyzed cow's milk protein or amino acids. This review is therefore written to assist clinicians to better understand the pathophysiologies of LI and CMA as well as to recognize the similarities and differences between clinical manifestations of LI and CMA.
Keywords: allergy; cow’s milk; lactase; lactose intolerance; protein.
Conflict of interest statement
N.S. is an employee of Danone Specialized Nutrition Indonesia. A.D. and K.R.S. have received funding for educational consultancy work from Danone Specialized Nutrition Indonesia. J.J. has no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fox A.T., Thomson M. Adverse reactions to cow’s milk. Pediatr. Child Health. 2007;17:288–294. doi: 10.1016/j.paed.2007.04.007. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

