Comparison of Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytopathology with Histopathological Examination of the Thyroid Gland in Patients Undergoing Elective Thyroid Surgery: Do We Still Need Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytopathology?
- PMID: 38337752
- PMCID: PMC10854902
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14030236
Comparison of Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytopathology with Histopathological Examination of the Thyroid Gland in Patients Undergoing Elective Thyroid Surgery: Do We Still Need Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytopathology?
Abstract
Background: The thyroid gland is responsible for various functions, but it is susceptible to pathologies. The gold standard for preliminarily diagnosing thyroid abnormalities is fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC), although it has some limitations; thus, postoperative histopathological examination confirms the diagnosis. The aim of the present study was to compare preoperative FNAC results with postoperative histopathological examination.
Methods: This study is a retrospective study based on FNAC and postoperative histopathology examination, which were compared and analyzed.
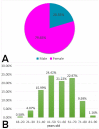
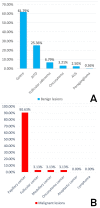
Results: This study included 344 patients between 18 and 86 years old (mean age: 53.06 ± 13.89), comprising 274 females and 70 males (mean ages 52.72 ± 13.86 and 54.39 ± 14.05, respectively) with a 3.9:1 female-to-male ratio. Statistical significance between the FNAC and histopathology results was observed (p = 0.0000), and 86 (25.00%) patients were found to have been diagnosed incorrectly based on FNAC. The sensitivity of FNAC was 92.31%, and its specificity was 82.08%, with positive and negative predictive values of 68.57% and 96.08%, respectively.
Conclusions: Due to many factors, FNAC may lead to over- or under-diagnosis, increasing the chances of complications associated with the selected treatment. However, we do not have any other more accurate tools; therefore, FNAC should still remain as the gold standard of preliminary examination.
Keywords: Bethesda classification; fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC); thyroid cancer; thyroid nodules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Armstrong M., Asuka E., Fingeret A. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2023. Physiology, Thyroid Function. - PubMed
-
- Irfan Ullah N.A., Ali S., Haq I.U., Khan I., Asif M. Study on the Prevalence of Goiter and Associated Factors Among Hospitalized Patients of District Timergara, Dir Lower Pakistan. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2022;41:32458–32463. doi: 10.26717/BJSTR.2022.41.006563. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

