Spatial Position and Anatomical Characteristics Associated with Impacted Third Molars Using a Map-Reading Strategy on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Scans: A Retrospective Analysis
- PMID: 38337776
- PMCID: PMC10855352
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14030260
Spatial Position and Anatomical Characteristics Associated with Impacted Third Molars Using a Map-Reading Strategy on Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Scans: A Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
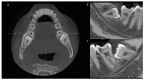
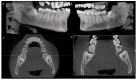
(1) Background: This study assessed the spatial position and anatomical features associated with impacted third molars through a map-reading strategy employing cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). (2) Methods: The positioning of impacted third molars on CBCT was assessed using Winter's and Pell and Gregory's classifications. External root resorption in mandibular second molars was categorized according to Herman's classification. Additionally, the relationship between the mandibular third molar root apex and the mandibular canal was examined. Comparative statistical analysis was conducted using Fisher's exact test, with a significance level considered as 5%. (3) Results: The results indicated that, based on Winter's classification, 48.06 % of impacted teeth were positioned mesioangularly. Employing Pell and Gregory's classification, 43.22% of the impacted molars fell into positions B and C, with 54.2% classified as Class II. A notable 69.7% of teeth exhibited no contact between the root apex and the mandibular canal, and external root resorption in the distal aspect of the second molar was absent in 88.7% of cases. (4) Conclusions: Utilizing the map-reading strategy with CBCT scans to assess the anatomical positions and characteristics of impacted third molars enhances professional confidence and sets a standard for quality and safety in the surgical procedure for patients.
Keywords: anatomy; cone-beam computed tomography; impacted third molar; inferior third molar; mandibular canal; surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The study was developed from the retrospective analysis of a database from a private radiological clinic. The author (Mike Reis Bueno) is a radiologist and was one of the examiners of the images. We believe that the fact that the author works at the place where the information is collected does not constitute a conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hatem M., Bugaughis I., Taher E. Pattern of third molar impaction in Libyan population: A retrospective radiographic study. Saudi. J. Dent. Res. 2016;7:7–12. doi: 10.1016/j.sjdr.2015.04.005. - DOI
-
- Carvalho J.R.S., Leite J.S., Oliveira R.S. Evaluation of impacted lower third molars using cone beam computed tomography. J. Dent. 2021;9:1–6.
-
- Oenning A.C.C., Neves F.S., Alencar P.N.B., Prado R.F., Groppo F.C., Haiter-Neto F. External root resorption of the second molar associated with third molar impaction: Comparison of panoramic radiography and cone beam computed tomography. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014;72:1444–1455. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2014.03.023. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

