Defense Regulatory Network Associated with circRNA in Rice in Response to Brown Planthopper Infestation
- PMID: 38337906
- PMCID: PMC10857171
- DOI: 10.3390/plants13030373
Defense Regulatory Network Associated with circRNA in Rice in Response to Brown Planthopper Infestation
Abstract
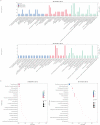
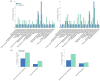
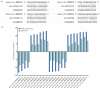
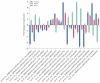
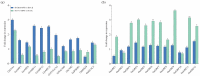
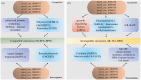
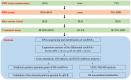
The brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens (Stål), a rice-specific pest, has risen to the top of the list of significant pathogens and insects in recent years. Host plant-mediated resistance is an efficient strategy for BPH control. Nonetheless, BPH resistance in rice cultivars has succumbed to the emergence of distinct virulent BPH populations. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) play a pivotal role in regulating plant-environment interactions; however, the mechanisms underlying their insect-resistant functions remain largely unexplored. In this study, we conducted an extensive genome-wide analysis using high-throughput sequencing to explore the response of rice circRNAs to BPH infestations. We identified a total of 186 circRNAs in IR56 rice across two distinct virulence groups: IR-IR56-BPH (referring to IR rice infested by IR56-BPH) and IR-TN1-BPH, along with a control group (IR-CK) without BPH infestation. Among them, 39 circRNAs were upregulated, and 43 circRNAs were downregulated in the comparison between IR-IR56-BPH and IR-CK. Furthermore, in comparison with IR-CK, 42 circRNAs exhibited upregulation in IR-TN1-BPH, while 42 circRNAs showed downregulation. The Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis revealed that the targets of differentially expressed circRNAs were considerably enriched in a multitude of biological processes closely linked to the response to BPH infestations. Furthermore, we assessed a total of 20 randomly selected circRNAs along with their corresponding expression levels. Moreover, we validated the regulatory impact of circRNAs on miRNAs and mRNAs. These findings have led us to construct a conceptual model that circRNA is associated with the defense regulatory network in rice, which is likely facilitated by the mediation of their parental genes and competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks. This model contributes to the understanding of several extensively studied processes in rice-BPH interactions.
Keywords: IR56 rice; Nilaparvata lugens; circular RNAs (circRNAs); rice-BPH interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Du B., Chen R.Z., Guo J.P., He G.C. Current understanding of the genomic, genetic, and molecular control of insect resistance in rice. Mol. Breed. 2020;40:24. doi: 10.1007/s11032-020-1103-3. - DOI
-
- Li C.P., Wu D.H., Huang S.H., Meng M., Shih H.T., Lai M.H., Chen L.J., Jena K.K., Hechanova S.L., Ke T.J., et al. The Bph45 gene confers resistance against brown planthopper in rice by reducing the production of limonene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24:1798. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021798. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

