Comprehensive Investigation of Ginsenosides in the Steamed Panax quinquefolius with Different Processing Conditions Using LC-MS
- PMID: 38338369
- PMCID: PMC10856252
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29030623
Comprehensive Investigation of Ginsenosides in the Steamed Panax quinquefolius with Different Processing Conditions Using LC-MS
Abstract
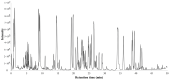
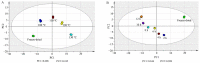
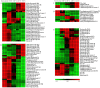
Panax quinquefolius (PQ) has been widely used in traditional Chinese medicine and functional food. Ginsenosides are the important functional components of PQ. The ginsenosides' diversity is deeply affected by the processing conditions. The ginsenosides in the steamed PQ have been not well-characterized yet because of the complexity of their structure. In the study, the comprehensive investigation of ginsenosides was performed on the steamed PQ with different steaming times and temperatures by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Based on the molecular weight, retention time and characterized fragment ions, 175 ginsenosides were unambiguously identified or tentatively characterized, including 45 protopanaxatriol type, 49 protopanaxadiol type, 19 octillol type, 6 oleanolic acid type ginsenosides, and 56 other ginsenosides. Ten new ginsenosides and three new aglycones were discovered in the steamed PQ samples through searching the database of CAS SciFindern. Principal component analysis showed the significant influence on the chemical components of PQ through different processing conditions. The steaming temperature was found to promote the transformation of ginsenosides more than the steaming time. The protoginsenosides were found to transform into the rare ginsenosides by elimination reactions. The malonyl ginsenosides were degraded into acetyl ginsenosides, and then degraded into neutral ginsenosides. The sugar chain experienced degradation, with position changes and configuration inversions. Furthermore, 20 (S/R)-ginsenoside Rh1, Rh2, Rg2, and Rh12 were found to transform from the S-configuration to the R-configuration significantly. This study could present a comprehensive ginsenosides profile of PQ with different steaming conditions, and provide technical support for the development and utilization of PQ.
Keywords: LC-MS; ginsenosides; identification; processing; steamed Panax quinquefolius.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
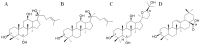
Similar articles
-
UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS Analysis for Steaming Times-dependent Profiling of Steamed Panax quinquefolius and Its Ginsenosides Transformations Induced by Repetitious Steaming.J Ginseng Res. 2012 Jul;36(3):277-90. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2012.36.3.277. J Ginseng Res. 2012. PMID: 23717129 Free PMC article.
-
An innovative processing driven efficient transformation of rare ginsenosides enhances anti-platelet aggregation potency of notoginseng by integrated analyses of processing-(chemical) profiling-pharmacodynamics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 30;319(Pt 1):117126. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117126. Epub 2023 Sep 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37716488
-
Intraconversion of Polar Ginsenosides, Their Transformation into Less-Polar Ginsenosides, and Ginsenoside Acetylation in Ginseng Flowers upon Baking and Steaming.Molecules. 2018 Mar 26;23(4):759. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040759. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29587462 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical analysis of Panax quinquefolius (North American ginseng): A review.J Chromatogr A. 2015 Dec 24;1426:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.11.012. Epub 2015 Nov 14. J Chromatogr A. 2015. PMID: 26643719 Review.
-
Advances in Saponin Diversity of Panax ginseng.Molecules. 2020 Jul 29;25(15):3452. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153452. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32751233 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the Variation in Antioxidant Activity and Chemical Composition upon the Repeated Thermal Treatment of the By-Product of the Red Ginseng Manufacturing Process.Molecules. 2024 Jun 28;29(13):3092. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133092. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38999042 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection and Enhanced Learning and Memory Abilities of Steamed American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolium L.) Based on Zebrafish.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jun 1;13(6):e70369. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70369. eCollection 2025 Jun. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40458084 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Elucidation and In Silico-Aided Toxicity Prediction of Forced Degradation Products of Ginsenoside Re Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Equipped with a Diode Array Detector and Charged Aerosol Detector (UHPLC-DAD-CAD) and Liquid Chromatography Coupled to a High-Resolution Mass Detector (LC-HRMS).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 10;25(24):13231. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413231. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39768996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hong H., Kim J., Lim T., Song Y., Cho C., Jang M. Mixing ratio optimization for functional complex extracts of rhodiolacrenulata, Panax quinquefolius, and astragalus membranaceus using mixturedesign and verification of immune functional efficacy in animal models. J. Funct. Foods. 2018;40:447–454. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.11.038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wei G., Yang F., Wei F., Zhang L., Gao Y., Qian J., Chen Z., Jia Z., Wang Y., Su H., et al. Metabolomes and transcriptomes revealed the saponin distribution in root tissues of Panax quinquefolius and Panax notoginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2020;44:757–769. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2019.05.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

