Density Functional Theory Studies on the Chemical Reactivity of Allyl Mercaptan and Its Derivatives
- PMID: 38338412
- PMCID: PMC10856204
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29030668
Density Functional Theory Studies on the Chemical Reactivity of Allyl Mercaptan and Its Derivatives
Abstract
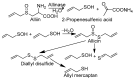
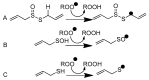
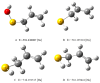
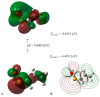
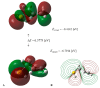
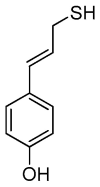
On the basis of density functional theory (DFT) at the B3LYP/cc-pVQZ level with the C-PCM solvation model, a comparative analysis of the reactivity of the garlic metabolites 2-propenesulfenic acid (PSA) and allyl mercaptan (AM, 2-propene-1-thiol) was performed. In particular, the thermodynamic descriptors (BDE, PA, ETE, AIP, PDE, and Gacidity) and global descriptors of chemical activity (ionization potential (IP), electron affinity (EA), chemical potential (μ), absolute electronegativity (χ), molecular hardness (η) and softness (S), electrophilicity index (ω), electro-donating (ω-) and electro-accepting (ω+) powers, and Ra and Rd indexes) were determined. The calculations revealed that PSA is more reactive than AM, but the latter may play a crucial role in the deactivation of free radicals due to its greater chemical stability and longer lifetime. The presence of a double bond in AM enables its polymerization, preserving the antiradical activity of the S-H group. This activity can be amplified by aryl-substituent-containing hydroxyl groups. The results of the calculations for the simplest phenol-AM derivative indicate that both the O-H and S-H moieties show greater antiradical activity in a vacuum and aqueous medium than the parent molecules. The results obtained prove that AM and its derivatives can be used not only as flavoring food additives but also as potent radical scavengers, protecting food, supplements, cosmetics, and drug ingredients from physicochemical decomposition caused by exogenous radicals.
Keywords: 2-propenesulfenic acid; DFT method; allyl mercaptan; chemical activity descriptors; garlic metabolites; thermodynamic descriptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hiramatsu K., Tsuneyoshi T., Ogawa T., Morihara N. Aged garlic extract enhances heme oxygenase-1 and glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit expression via the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway in human endothelial cells. Nutr. Res. 2016;36:143–149. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2015.09.018. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

