Chemical Epigenetic Regulation Secondary Metabolites Derived from Aspergillus sydowii DL1045 with Inhibitory Activities for Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases
- PMID: 38338416
- PMCID: PMC10856041
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29030670
Chemical Epigenetic Regulation Secondary Metabolites Derived from Aspergillus sydowii DL1045 with Inhibitory Activities for Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases
Abstract
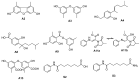
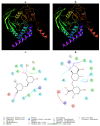
Protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) are ubiquitous in living organisms and are promising drug targets for cancer, diabetes/obesity, and autoimmune disorders. In this study, a histone deacetylase inhibitor called suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) was added to a culture of marine fungi (Aspergillus sydowii DL1045) to identify potential drug candidates related to PTP inhibition. Then, the profile of the induced metabolites was characterized using an integrated metabolomics strategy. In total, 46% of the total SMs were regulated secondary metabolites (SMs), among which 20 newly biosynthesized metabolites (10% of the total SMs) were identified only in chemical epigenetic regulation (CER) broth. One was identified as a novel compound, and fourteen compounds were identified from Aspergillus sydowii first. SAHA derivatives were also biotransformed by A. sydowii DL1045, and five of these derivatives were identified. Based on the bioassay, some of the newly synthesized metabolites exhibited inhibitory effects on PTPs. The novel compound sydowimide A (A11) inhibited Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 (SHP1), T-cell protein tyrosine phosphatase (TCPTP) and leukocyte common antigen (CD45), with IC50 values of 1.5, 2.4 and 18.83 μM, respectively. Diorcinol (A3) displayed the strongest inhibitory effect on SHP1, with an IC50 value of 0.96 μM. The structure-activity relationship analysis and docking studies of A3 analogs indicated that the substitution of the carboxyl group reduced the activity of A3. Research has demonstrated that CER positively impacts changes in the secondary metabolic patterns of A. sydowii DL1045. The compounds produced through this approach will provide valuable insights for the creation and advancement of novel drug candidates related to PTP inhibition.
Keywords: Aspergillus sydowii; chemical epigenetic regulation (CER); protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs); secondary metabolites (SMs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Metabolomic Strategy to Characterize the Profile of Secondary Metabolites in Aspergillus aculeatus DL1011 Regulated by Chemical Epigenetic Agents.Molecules. 2022 Dec 26;28(1):218. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010218. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615412 Free PMC article.
-
An epigenetic modifier induces production of (10'S)-verruculide B, an inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases by Phoma sp. nov. LG0217, a fungal endophyte of Parkinsonia microphylla.Bioorg Med Chem. 2017 Mar 15;25(6):1860-1866. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.048. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28202316 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a new biphenyl derivative by epigenetic manipulation of marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor.Nat Prod Res. 2019 Apr;33(8):1191-1195. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1465423. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Nat Prod Res. 2019. PMID: 29683350
-
Secondary Metabolites, Biological Activities, and Industrial and Biotechnological Importance of Aspergillus sydowii.Mar Drugs. 2023 Aug 5;21(8):441. doi: 10.3390/md21080441. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37623723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Advances of Bioactive Sesquiterpenoids Isolated from Marine-Derived Aspergillus sp.Molecules. 2022 Oct 30;27(21):7376. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217376. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Update of Fungal Endophyte Diversity and Strategies for Augmenting Therapeutic Potential of their Potent Metabolites: Recent Advancement.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 May;197(5):2799-2866. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-05098-9. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39907846 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ibrahim S., Mohamed S., Alsaadi B., Althubyani M., Awari Z., Hussein H., Aljohani A., Albasri J., Faraj S., Mohamed G. Secondary metabolites, biological activities, and industrial and biotechnological importance of Aspergillus sydowii. Mar. Drugs. 2023;21:441. doi: 10.3390/md21080441. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

