Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Photodynamic Treatment with Curcuma L. and Trans-Cinnamaldehyde against Listeria monocytogenes
- PMID: 38338429
- PMCID: PMC10856099
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29030685
Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effects of Photodynamic Treatment with Curcuma L. and Trans-Cinnamaldehyde against Listeria monocytogenes
Abstract
Photodynamic inactivation (PDI) is a highly effective treatment that can eliminate harmful microorganisms in a variety of settings. This study explored the efficacy of a curcumin-rich extract, Curcuma L., (Cur)- and essential oil component, trans-cinnamaldehyde, (Ca)-mediated PDI against Listeria monocytogenes ATCC 15313 (Lm) including planktonic cells and established biofilms on silicone rubber (Si), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), stainless steel 316 (SS), and polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Applying Ca- and Cur-mediated PDI resulted in planktonic cell reductions of 2.7 and 6.4 log CFU/cm2, respectively. Flow cytometric measurements (FCMs) coupled with CFDA/PI and TOTO®-1 staining evidenced that Ca- doubled and Cur-mediated PDI quadrupled the cell damage. Moreover, the enzymatic activity of Lm cells was considerably reduced by Cur-mediated PDI, indicating its superior efficacy. Photosensitization also affected Lm biofilms, but their reduction did not exceed 3.7 log CFU/cm2. Cur-mediated PDI effectively impaired cells on PET and PTFE, while Ca-mediated PDI caused no (TOTO®-1) or only slight (PI) cell damage, sparing the activity of cells. In turn, applying Ca-mediate PDI to Si largely diminished the enzymatic activity in Lm. SS contained 20% dead cells, suggesting that SS itself impacts Lm viability. In addition, the efficacy of Ca-mediated PDI was enhanced on the SS, leading to increased damage to the cells. The weakened viability of Lm on Si and SS could be linked to unfavorable interactions with the surfaces, resulting in a better effect of Ca against Lm. In conclusion, Cur demonstrated excellent photosensitizing properties against Lm in both planktonic and biofilm states. The efficacy of Ca was lower than that of Cur. However, Ca bears potent antibiofilm effects, which vary depending on the surface on which Lm resides. Therefore, this study may help identify more effective plant-based compounds to combat L. monocytogenes in an environmentally sustainable manner.
Keywords: Curcuma L.; Listeria monocytogenes; biofilms; flow cytometry; photodynamic inactivation; trans-cinnamaldehyde.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

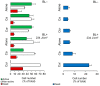
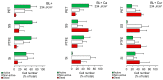


Similar articles
-
Prevention of surface colonization and anti-biofilm effect of selected phytochemicals against Listeria innocua strain.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023 Aug;228:113391. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2023.113391. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023. PMID: 37290199
-
Inactivation of dried cells and biofilms of Listeria monocytogenes by exposure to blue light at different wavelengths and the influence of surface materials.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Oct 31;89(10):e0114723. doi: 10.1128/aem.01147-23. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37846990 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of antibiofilm efficacy of essential oil components β-caryophyllene, cinnamaldehyde and eugenol alone and in combination against biofilm formation and preformed biofilms of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella typhimurium.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2020 Aug;71(2):195-202. doi: 10.1111/lam.13308. Epub 2020 May 29. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32357268
-
Biofilm formation and desiccation survival of Listeria monocytogenes with microbiota on mushroom processing surfaces and the effect of cleaning and disinfection.Int J Food Microbiol. 2024 Feb 2;411:110509. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2023.110509. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Int J Food Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38101188
-
New trends in the development of photodynamic inactivation against planktonic microorganisms and their biofilms in food system.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2023 Sep;22(5):3814-3846. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.13215. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2023. PMID: 37530552 Review.
Cited by
-
Improvement of Selected Quality and Safety Traits in Turmeric-Enriched Kale Pesto Using Blue Light and Sous-Vide.Molecules. 2024 Dec 11;29(24):5831. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245831. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39769920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodríguez-Campos D., Rodríguez-Melcón C., Alonso-Calleja C., Capita R. Persistent Listeria monocytogenes isolates from a poultry-processing facility form more biofilm but do not have a greater resistance to disinfectants than sporadic strains. Pathogens. 2019;8:250. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040250. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y., Leung A.W., Hua H., Rao X., Xu C. Photodynamic action of LED-activated curcumin against Staphylococcus aureus involving intracellular ROS increase and membrane damage. Int. J. Photoenergy. 2014;2014:637601. doi: 10.1155/2014/637601. - DOI
-
- Costa L., Tomé J.P., Neves M.G., Tomé A.C., Cavaleiro J.A., Faustino M.A., Cunha Â., Gomes N.C., Almeida A. Evaluation of resistance development and viability recovery by a non-enveloped virus after repeated cycles of aPDT. Antiviral Res. 2011;91:278–282. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.06.007. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

