A Novel Approach to Serving Plant-Based Confectionery-The Employment of Spray Drying in the Production of Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Delivery Systems Enriched with Teucrium montanum L. Extract
- PMID: 38338507
- PMCID: PMC10855723
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13030372
A Novel Approach to Serving Plant-Based Confectionery-The Employment of Spray Drying in the Production of Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Delivery Systems Enriched with Teucrium montanum L. Extract
Abstract
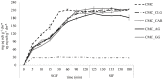
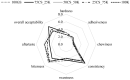
In this study, spray drying was used as a technological solution for the valorization of Teucrium montanum extract into carboxymethyl cellulose-based delivery systems (CMC), individually or in combination with collagen, guar gum, gum arabic, and kappa-carrageenan. The results showed that the process yield and morphological properties were positively influenced by the introduction of CMC binary blends. The employment of CMC resulted in a high encapsulation efficiency (77-96%) for all phenylethanoid glycosides (PGs) analyzed. Due to the low wettability of the microparticles, a relatively gradual in vitro release of the PGs was achieved. Infusion of the filling with hydrophilic T. montanum extract encapsulated in microparticles with high hydrophobic surface area proved to be a practical route for significant confectionery fortification (5-9 mg PGs per dw serving), ensuring prolonged interaction between the food matrix used and the extract under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Based on sensory evaluation, the introduction of kudzu starch into the jelly matrix has shown a texture-modifying potential.
Keywords: carboxymethyl cellulose; encapsulation; jelly candy; kudzu starch; microparticles; phenylethanoid glycosides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Teucrium montanum L.-Unrecognized Source of Phenylethanoid Glycosides: Green Extraction Approach and Elucidation of Phenolic Compounds via NMR and UHPLC-HR MS/MS.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 24;12(11):1903. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111903. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001756 Free PMC article.
-
Microencapsulation of fingered citron extract with gum arabic, modified starch, whey protein, and maltodextrin using spray drying.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Jun 1;152:1125-1134. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.201. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 31751737
-
Characterization of starch and gum arabic-maltodextrin microparticles encapsulating acacia tannin extract and evaluation of their potential use in ruminant nutrition.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2019 Jul;32(7):977-987. doi: 10.5713/ajas.18.0632. Epub 2018 Nov 28. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2019. PMID: 30744376 Free PMC article.
-
Current Research on Spray-Dried Chitosan Nanocomposite Microparticles for Pulmonary Drug Delivery.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023;11(2):127-137. doi: 10.2174/2211738511666221128093822. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36443972 Review.
-
Encapsulation of Bioactive Compounds for Food and Agricultural Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Oct 6;14(19):4194. doi: 10.3390/polym14194194. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36236142 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biofortification of Acacia and Polyflower Honey with Pine sylvestris L. Bud Extracts: Exploring Antioxidant Variation Across Developmental Stages for Enhanced Nutritional Value.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025 Jan 25;80(1):47. doi: 10.1007/s11130-024-01282-8. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39862277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fatiha B.A., Ouafae B., Souad S., Fatima E.H., Jamila D., Allal D., Lahcen Z. Ethnobotany study of medicinal plants used in the treatment of respiratory diseases in the middle region of Oum Rbai. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017;2:1460–1468. doi: 10.22161/ijeab/2.4.3. - DOI
-
- Savić J., Mačukanović-Jocić M., Jarić S. Medical ethnobotany on the Javor mountain (Bosnia and Herzegovina) Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2019;27:52–64. doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2019.02.007. - DOI
-
- Olcha P., Winiarska-Mieczan A., Kwiecień M., Nowakowski Ł., Miturski A., Semczuk A., Kiczorowska B., Gałczyński K. Antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-obesogenic, and antidiabetic properties of tea polyphenols-the positive impact of regular tea consumption as an element of prophylaxis and pharmacotherapy support in endometrial cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:6703. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126703. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

