Migration of Nutrient Substances and Characteristic Changes of Chicken White Soup Emulsion from Chicken Skeleton during Cooking
- PMID: 38338545
- PMCID: PMC10855391
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13030410
Migration of Nutrient Substances and Characteristic Changes of Chicken White Soup Emulsion from Chicken Skeleton during Cooking
Abstract
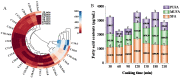
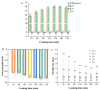
The protein and fat in chicken skeleton can be emulsified in a boiling state to form milky white chicken soup. White chicken soup has a delicious taste, good nutritional value, a beautiful color, and volatile flavor compounds. However, cooking time significantly impacts the quality of white chicken soup. Herein, we investigated the influence of cooking time (30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, and 210 min) on the migration of nutrient substances and characteristics changes in white chicken soup from chicken skeletons. The results showed that nutrients such as total lipids, water-soluble protein, total sugars, solid matter, and oligopeptides in the chicken skeletons' tissue continuously migrated into the soup during the cooking process. The total nutrient content in the chicken soup was highest after cooking for 180 min. Simultaneously, the white chicken soup obtained after cooking for 180 min had low interfacial tension and high whiteness, viscosity, and storage stability. The high stability index was associated with increased ζ potential and decreased particle size. The contact angle analysis results also indicated that the stability of the white chicken soup was improved when the cooking time reached 180 min. This research provides basic information for the production of high-quality white chicken soup.
Keywords: interfacial behavior; migration; nutrient substances; stability; white chicken soup.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Meng Q., Zhou J.W., Gao D., Xu E.B., Guo M.M., Liu D.H. Desorption of nutrients and flavor compounds formation during the cooking of bone soup. Food Control. 2022;132:108408. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108408. - DOI
-
- Zhang J., Zhu L.H., Li H.H., Tang H.G., Yang H.J., Zhao K., Kong F.B., Yin T., Yao Q., Chen L.H. Effects of micro-/nano-scaled chicken bones on heat- induced gel properties of low-salt pork batter: Physicochemical characteristics, water distribution, texture, and microstructure. Food Chem. 2021;373:131574. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131574. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Akramzadeh N., Ramezani Z., Ferdousi R., Akbari-Adergani B., Mohammadi A., Karimian-khosroshahi N., Famenin B.K., Pilevar Z., Hosseini H. Effect of chicken raw materials on physicochemical and microbiological properties of mechanically deboned chicken meat. Vet. Res. Forum. 2020;11:153–158. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2018.90365.2186. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

