Study on the Effect of Microwaved Brewer's Spent Grains on the Quality and Flavor Characteristics of Bread
- PMID: 38338596
- PMCID: PMC10855328
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13030461
Study on the Effect of Microwaved Brewer's Spent Grains on the Quality and Flavor Characteristics of Bread
Abstract
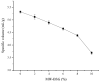
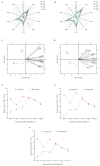
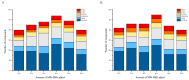
To enable a wider utilization of co-products from beer processing and minimize the negative effect of added grain on bread quality, flavor, and other attributes, brewer's spent grains (BSG) are processed through microwave pretreatment, and then the microwave-treated BSG (MW-BSG) is added to bread. So far, there has been no investigation on the effect of microwave-pretreated BSG on bread quality and flavor. In this study, we examined the effects of diverse microwave treatment variables on the physicochemical structure of BSG and explored the consequences of MW-BSG on the quality and flavor of bread. The results showed that soluble dietary fiber and water-soluble protein levels in MW-BSG increased significantly (144.88% and 23.35%) at a 540 W microwave power, 3 min processing time, and 1:5 material-liquid ratio of BSG to water. The proper addition of MW-BSG positively affected the bread texture properties and color, but excessive amounts led to an irregular size and distribution of the bread crumbs. The result of electronic nose and HS-SPME-GC-MS analyses showed that the addition of MW-BSG modified the odor profile of the bread. A sensory evaluation showed mean scores ranging from 6.81 to 4.41 for bread containing 0-10% MW-BSG. Consumers found a maximum level of 6% MW-BSG acceptable. This study endeavors to decrease environmental contamination caused by brewing waste by broadening the methods by which beer co-products can be utilized through an innovative approach.
Keywords: BSG; bread; dietary fiber; electronic nose; microwave treatment; protein; sensory evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lynch K.M., Steffen E.J., Arendt E.K. Brewers’ spent grain: A review with an emphasis on food and health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016;122:553–568. doi: 10.1002/jib.363. - DOI
-
- Ye S., Shah B.R., Li J., Liang H., Zhan F., Geng F., Li B. A critical review on interplay between dietary fibers and gut microbiota. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022;124:237–249. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.04.010. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

